
Precision agriculture in india
“A friend of mine, Suresh Yadav, who runs a 15-acre farm in Haryana, used to use traditional methods. But when he used drone-based spraying and soil health monitoring tools, his wheat yield increased by up to 20%. This is the power of precision agriculture!”
Precision agriculture in India is not just a concept today but is becoming a revolution. According to the latest reports of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), through satellite imaging, IoT sensors, and AI-based analysis, farmers can reduce water usage by up to 30% and increase cost efficiency by using fertilizers correctly.
But the question is—can every farmer adopt precision agriculture in India? Is it affordable and scalable in a developing nation like India? In this blog, we will see how AI, drones, and remote sensing technologies are ushering in a new era in Indian agriculture and how both small and large farmers can benefit from it.
What is Precision agriculture
Precision Agriculture is an advanced farming approach that uses technology, data analytics, and AI to improve crop yield and best optimize inputs (water, fertilizer, pesticide).
🔹 Key Technologies in Precision Agriculture:
✔️ GPS-guided tractors – These allow accurate sowing and plowing in fields.
✔️ Drones & Remote Sensing – These help in soil health and pest detection.
✔️ IoT-Based Soil Sensors – These monitor real-time moisture and nutrient levels.
Precision agriculture, also called modern agriculture, is a type of farming technique
Expert Opinion & Research:
According to a latest study by ICAR, water usage can be reduced by 30-50% through precision farming, which is a big step towards sustainable agriculture. Similarly, the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) says that if Indian farmers adopt precision agriculture, both food security and economic growth can improve.
50% of agriculture in India is monsoon-dependent, and challenges like water scarcity, soil degradation, and high input costs are impacting productivity. Precision agriculture in India is a scientific solution to these problems.
Key Reasons for Adoption:
🔹 Water shortage: According to FAO, 80% of India’s freshwater is used in agriculture, which can be optimized by precision irrigation.
🔹 Soil fertility loss: According to research by ICAR, 95% of Indian soils have micronutrient deficiency, which can be solved by site-specific nutrient management.
🔹 High input cost & low yield: Smart farming techniques reduce fertilizer and pesticide wastage and improve yield.
🔹 Impact of Climate Change: IoT and AI-based monitoring allow early detection of unpredictable weather and pest attacks.
But is it affordable for every farmer? Next we will see how government schemes and subsidies can help in this.
Benefits of Precision Agriculture in India
Precision agriculture is more efficient and sustainable than traditional farming. This technology-driven approach improves yield and reduces input costs. Now let’s look at the top 6 benefits due to which precision agriculture in India is becoming popular in India
Top Benefits of Precision Agriculture:
✅ 1. Higher Crop Yield & Productivity
- According to an ICAR study, precision farming can increase wheat and rice production by 15-20%.
- Drones and remote sensing improve crop health monitoring, which helps in timely disease control.
✅2. Efficient Resource Usage
With the help of mobile applications like Plantix, Agro Star, and Agro Tech, applications, accurate details of all the resources used from the sowing of crops to harvesting reach the farmers through these applications and our farmers can decide when to use the best resources.
✅ 3. Reduced Water Consumption
- According to the FAO, 80% of India’s fresh water is used in agriculture, and smart irrigation can save up to 30-40% of water.
- Drip and sensor-based irrigation provide water only as per requirement, which avoids over-irrigation.
✅ 4. Cost Savings in Fertilizers & Pesticides
- Precision agriculture uses Site-Specific Nutrient Management (SSNM), which ensures the use of fertilizers as per the actual requirement of the soil.
- According to a report by Punjab Agricultural University(PAU), there can be a reduction of up to 25-30% in fertilizer and pesticide costs.

✅ 5. Better Profitability for Farmers
- The use of smart technologies like GPS, GIS, and drones increases profit margins due to cost efficiency and better yield.
- Digital farming tools help farmers analyse market demand and price trends, which gives them better price realisation.
✅6. Early Pest and Disease Detection
Plantix, Agro Central, Farm Wish, and Agro Tech are all mobile applications that detect diseases and pests that affect crops before they attack and provide step-by-step solutions for them. It also provides information on parameters such as usage, dosage and other chemicals like fungicides, insecticides etc.
Final Thought:
Precision agriculture in India can be a game-changer for both small and big farmers. However, its widespread adoption will happen only when farmers get proper training and government support.

Challenges in Precision Agriculture in India
Precision agriculture in India has just been introduced in India, so farmers face some problems adopting it. These are given below…
1. High Initial Costs
Advanced tools like drones, GPS systems, modern software tools and sensors require more investment than traditional farming equipment. For example, purchasing a drone for crop monitoring can cost over ₹1.5 lakh to 2 lakh. Small farmers in India often struggle to afford such technologies without support, subsidies or financial assistance. There are some solutions
Solution-
- Government Help: Provide more subsidies or low-interest loans to help farmers afford expensive tools.
- Rent Equipment: Set up places where farmers can rent drones, GPS systems, and other tools instead of buying them.
- Share Equipment: Encourage farmers to share expensive equipment through local groups or cooperatives.
- Cheaper Options: Create simpler, low-cost versions of modern farming tools for small farmers.
- Easy Financing: Offer easy payment plans or insurance to help farmers pay for new equipment.
2. Limited Awareness to precision farming
Many farmers, especially rural farmers, are unaware of precision agriculture in India, farming and technologies. For instance, surveys in villages of Uttar Pradesh have shown that most farmers have never heard of soil sensors, GPS technology or IoT-based farming. Awareness campaigns, education and demonstrations are needed to bridge this gap and provide new technology. There are some solutions for precision agriculture in India
Solution-
- Awareness Campaigns: Use radio, TV, and social media to tell farmers about new farming technologies.
- Training Programs: Offer free classes or workshops to teach farmers how to use modern farming tools.
- Demonstration Farms: Set up farms where farmers can see how new technologies work and learn to use them.
- Local Support: Work with local agricultural workers to help farmers learn and adopt new techniques.
- Mobile Learning: Create apps or text messages with simple farming tips and lessons on new technologies.
3. Poor Internet Connectivity
Precision agriculture relies on IoT to monitor and manage farming activities in real time. However, in remote areas like Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh, poor internet connectivity makes it difficult to use these systems. Without reliable internet, farmers can’t access real-time data for better decision-making. This limits the benefits of IoT tools, reducing their impact on productivity and efficiency. There are some solutions Precision agriculture in india
Solutions-
LoRa and Mesh Networks: Low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) like LoRa or mesh networks can help in remote areas.
Offline Data Logging and Syncing: Devices can collect and store data locally and sync it with a centralized system when connectivity is available.
Satellite Internet: Technologies like Starlink or other satellite-based internet solutions can provide connectivity to remote regions, through satellite.
Edge Computing: Instead of sending all data to the cloud, edge computing allows data processing at or near the data source. This minimizes reliance on constant internet connectivity.
Government and Private Partnerships: Encouraging investment in rural internet infrastructure for private internet providers.

3. Landholdings Problem
In Bihar, most farms are smaller than one hectare, making it hard to use tools like GPS-guided tractors. The fields are small and spread out, so these technologies don’t work efficiently. This creates challenges for farmers, showing the need for affordable and simple solutions for small farms. There are some solutions for Precision agriculture in india
Solutions-
- Shared Equipment: Farmers can share tools like GPS-guided tractors through cooperatives or groups.
- Rental Services: Set up centres where farmers can rent precision tools as needed.
- Affordable Tools: Develop smaller, low-cost versions of precision farming equipment.
- Government Support: Provide subsidies or loans for small farmers to access new technologies.
- Training Programs: Educate farmers on using affordable precision methods effectively
4. Skill Gaps and Training Needs
Farmers often lack the technical knowledge to operate equipment. For example, farmers in Tamil Nadu who were introduced to drone technology faced difficulties in managing the software and interpreting aerial imagery without adequate training.
- Training Programs: Offer hands-on training to teach farmers how to use new technologies like drones.
- User-Friendly Software: Develop simpler, easy-to-understand software for farmers.
- Local Support Centers: Set up local help desks or experts to assist farmers with technology issues.
- Online Tutorials: Provide accessible video tutorials and guides for self-learning.
- Provide Networks: Create peer networks for experienced farmers to mentor others
5. Data Management Issues
Collecting data is only the first step, analyzing it is equally important. For instance, farmers in Maharashtra using soil health monitoring systems reported difficulty understanding the data outputs due to a lack of simple, user-friendly analytics tools. There are some solutions for Precision agriculture in india
Solutions-
- Simple Analytics Tools: Develop easy-to-use software with clear, visual reports to help farmers understand the data.
- Mobile Apps: Create mobile apps that translate complex data into simple insights.
- Training on Data Interpretation: Offer workshops and tutorials to help farmers understand how to analyze soil data.
- Real-time Assistance: Provide access to support centres or online chat for real-time help in interpreting data.
- Local Experts: Employ local agronomists to explain data and give personalized recommendations.
6. Dependence on Weather Conditions
Precision agriculture depends on stable weather for accurate predictions. For example, unpredictable monsoon patterns in Karnataka and UP often disrupt irrigation schedules designed by IoT-based systems, leading to inefficiencies. There are some solutions for Precision agriculture in India
Solution-
- Weather Forecast Integration: Integrate reliable weather forecast data into irrigation systems to help farmers plan better.
- Backup Systems: Implement backup irrigation methods, like rainwater harvesting, to mitigate disruptions.
- Farmers’ Alerts: Send farmers weather alerts through mobile apps to enable timely adjustments to their irrigation plans.
- Flexible Technology: Create systems that are adaptable.
7. Insufficient Government Support
While programs like Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana aim to promote efficient water use, many farmers report delays in accessing subsidies for precision equipment. For example, farmers in Gujarat faced long waiting periods for drip irrigation subsidies, discouraging adoption.
Solution-
- Application Process: Simplify the paperwork and approval process for quicker subsidy access.
- Digital Platforms: Set up online platforms to speed up subsidy applications and approvals.
- Timely Disbursement: Ensure faster processing and timely disbursement of funds to prevent delays.
- Awareness Campaigns: Run programs to inform farmers about available subsidies and the application process.
- Local Support Centers: Establish local offices or agents to assist farmers in accessing and processing subsidy requests efficiently.
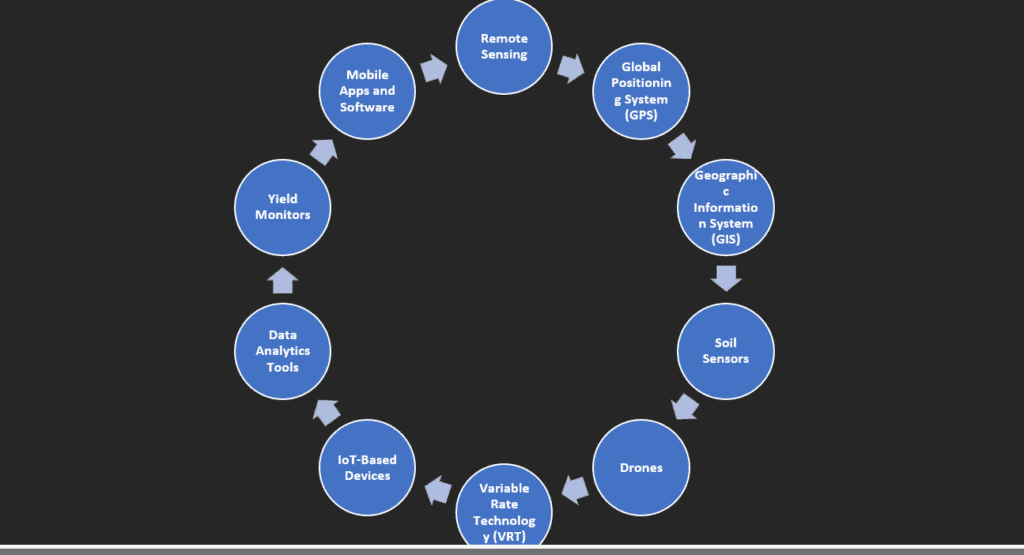
Basic components/tools of precision farming in India
This is the few component of Precision agriculture in India
- Remote Sensing
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Geographic Information System (GIS)
- Soil Sensors
- Drones
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT)
- IoT-Based Devices
- Data Analytics Tools
- Yield Monitors
- Mobile Apps and Software
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is a technology-driven approach that uses satellite and drone imagery for real-time field monitoring and data analysis. This provides farmers with accurate data on soil health, crop condition, and water availability, which helps in better decision-making and high productivity.
✅ Example: Satellites like NASA’s Landsat and ISRO‘s RISAT regularly monitor Indian farmlands through remote sensing.
History of Remote Sensing-
Remote sensing began in the 19th century with aerial photography used for mapping. In the 20th century, satellite technology advanced the field, and the launch of Landsat satellites in the 1970s revolutionized agriculture by providing high-resolution images for monitoring crops and soil.
History of Remote Sensing in India-
The use of remote sensing in India started in the 1970s when ISRO launched its first earth observation program.
🔹 1988: ISRO launched the IRS-1A satellite, India’s first dedicated remote sensing satellite.
🔹 2003: RISAT (Radar Imaging Satellite) was launched, which can monitor even inside cloud cover.
🔹 2019: Cartosat-3 was launched, which has sub-meter resolution imaging capability, which helps in agriculture mapping and crop health analysis.
✅ Fact: Today, India has 13+ active remote sensing satellites, which are working in agriculture, disaster management, and climate monitoring.

this image was taken by space-x
Components of Remote Sensing
Components-
Sensors: Devices that capture data (e.g., cameras, radiometers, LiDAR).
Platforms: Carriers of sensors such as satellites, drones, or aircraft.
Data Processing Tools: Software that processes and analyzes the captured data.
Types of Remote Sensing
Passive Remote Sensing: Relies on natural sunlight to capture images (e.g., satellite imagery). It is the work on sunlight signal.
Active Remote Sensing: Emits its signals and measures the reflection (e.g., radar, LiDAR). It is the work on radiation signals.
Advantages of Remote Sensing in Precision Agriculture in India
Increased Efficiency
Higher Yields
Cost Savings
Environmental Benefits
Data-Driven Decisions
Early Problem Detection
Sustainability
Disadvantages of Remote Sensing in Precision Agriculture in India
High Initial Investment
Technical Knowledge Required
Limited Accessibility
Weather Dependence
Maintenance Costs
Data Overload
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system used for accurate location tracking and mapping. In precision agriculture, GPS is used for tractor guidance, variable rate technology (VRT), and yield mapping, which makes farming more efficient and cost-effective.
✅ Example:
Farmers are doing accurate sowing and fertilizer application using GPS-enabled tractors and drones.
In India, ISRO’s NavIC system is also an alternative to GPS, which provides even more accurate data for Indian farmers.
History of GPS
The United States Department of Defense developed GPS technology in the 1970s, and it became fully operational in the 1990s. Initially used for military navigation.
History of GPS in India
India adopted GPS technology in the 1990s for various applications, including agriculture. Today, GPS-based tools and services are widely used by Indian farmers for field mapping, Field and yield monitoring, fertilizer and irrigation management and precision Farming. Available Indigenous systems like the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS).
Component of Global Positioning System (GPS)
There are 3 most important components used in GPS…
Space Segment: Satellites orbiting Earth that transmit positioning signals.
Control Segment: Ground stations that monitor, control, and maintain satellite accuracy.
User Segment: GPS receivers are used to calculate precise location and time.
Type of Global Positioning System (GPS)
Standard GPS: Suitable for general navigation with moderate accuracy.
Differential GPS (DGPS): Provides higher accuracy.
Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS: Ideal with precision agriculture tasks like planting and spraying.
Advantages of GPS in Precision Agriculture in India
- High Accuracy
- Cost Savings
- Time Efficiency
- Environmental Benefits
- User-Friendly
Disadvantages of GPS in Precision Agriculture in India
- High Initial Cost
- Signal Limitations
- Training Needs
- Maintenance Costs
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a digital mapping technology that collects, analyzes, and visualizes spatial data. In precision agriculture, GIS is used for farm mapping, soil health monitoring, yield prediction, and resource optimization.
✅ Example:
Indian farmers are improving soil fertility and irrigation planning by using GIS-based maps.
ISRO’s Bhuvan portal and ICAR’s GIS-based soil health mapping projects have boosted precision farming.
History of GIS
GIS technology began in the 1960s to assist with mapping and analyzing geographic data.
History of GIS in India
India started using GIS in the 1980s, mainly for urban planning and resource management. Its use in agriculture grew with programs like the National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI) and Digital India.
Components of GIS
Hardware: Computers, GPS devices, and drones that collect and process geographic data.
Software: Programs like ArcGIS, QGIS, and GRASS allow users to analyze and visualize data.
Data: Includes satellite images, maps, and information about soil and crops.
Type of GIS
Desktop GIS: Used on personal computers for local data analysis.
Web GIS: Online platforms that provide access to GIS data and tools.
Mobile GIS: Apps on smartphones or tablets for fieldwork and data collection.
Enterprise GIS: Large-scale systems. manage data across multiple departments.
Advantages of GIS in Precision Agriculture in India
Accurate Decisions
Saves Resources
Cost-Effective
Supports Sustainability
Real-Time Monitoring
- Time management
Disadvantages of GIS in Precision Agriculture in India
High Costs
Training Needs
Data Accuracy problem
Infrastructure Issues
Maintenance Cost

Top 5 mobile apps precision agriculture in India
In today’s digital era, precision agriculture has become a powerful tool for data-driven decision-making and smart farming. Through mobile apps, Indian farmers can do real-time weather updates, soil health analysis, pest management and crop monitoring.
📌 Example:
Soybean farmers of Madhya Pradesh reduced pesticide costs by 20% by using the Kisan Suvidha App.
Grape farmers of Maharashtra are optimising irrigation and fertilizer schedules through the FARMCONNECT app.
Let’s see the top 5 mobile apps that help Indian farmers in precision agriculture.
1. Kisan Suvidha (Government of India)
✅ Features: Weather forecast, market price, soil health, advisory services.
✅ Why It’s Important: This app launched by the Ministry of Agriculture is a multi-purpose solution that provides weather, market price and crop advisory to farmers.
2. FARMCONNECT (ICAR & IIT-Kanpur)
✅ Features: Soil & water analysis, AI-based crop disease detection, satellite imaging.
✅ Why It’s Important: This AI-powered app from ICAR and IIT-Kanpur gives real-time precision farming insights to farmers.
3. AgriApp
✅ Features: Fertilizer recommendation, soil health reports, organic farming guidance.
✅ Why It’s Important: Farmers can do crop-specific guidance and fertilizer management through AgriApp.
4. Krishi Network
✅ Features: Expert consultation, weather updates, agri news.
✅ Why It’s Important: Indian farmers can connect directly to agriculture experts through Krishi Network.
5. BharatAgri
✅ Features: AI-based farm analytics, irrigation schedule, disease prediction.
✅ Why It’s Important: Helps in smart farming and AI-driven decision-making.
what is the role of precision agriculture in India agriculture?
There are some roles in precision agriculture in India…
Better Use of Resources
Water:
In India, many areas face water shortages. Precision farming helps farmers use water wisely by monitoring soil moisture and controlling irrigation systems.
Fertilizers and Pesticides:
Precision agriculture uses sensors to apply fertilizers and pesticides only where they are needed
Increased Crop Production
Using tools like drones and satellites, farmers can take action quickly to improve crop health, and management field leading to higher yields.
Healthier Soil
With sensors, GPS, GIS and other technology, farmers can check the health of their soil regularly. Precision agriculture tells them what nutrients the soil needs, so they can add only what’s necessary.
Early Disease and Pest Detection
Drones and sensors can spot pests or diseases early, allowing farmers to treat affected areas right away. This helps prevent crop damage and reduces the use of harmful chemicals.
Lower Costs
Precision agriculture helps farmers use optimum resources like water, fertilizers, and pesticides by applying them only where needed. This reduces overall costs and helps farmers save money.
Adaptation to Climate
Weather is unpredictable, especially in India, and crops can suffer. Precision farming uses weather data and sensors to help farmers plan better for extreme weather conditions, like droughts or floods.
Helping Small Farmers
Precision agriculture is not just for large farms. Small farmers can also use affordable tools like mobile apps and simple sensors to improve their farming practices,
Status of Precision Farming in India
The adoption of precision farming is slowly increasing in India. Its adoption in large-scale farms is 15-18%, while it is only 5% among small farmers. Because of technology and high investment, it is not becoming popular. Its adoption is good in Punjab and Maharashtra, but in states like Bihar and Odisha, this adoption is still very low.
1. Precision farming has arrived in India in recent years and is still in its initial stages. Interest in precision farming is increasing among farmers seeking higher yields.
2. The Government of India has initiated various projects and programs to promote precision farming and modern technology. These include schemes like Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana, Digital India Program, National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture, etc.
3. Farmers are being made aware of the benefits and uses of precision farming. In addition to this, technical assistance is provided.
4. Many private companies and startups are also active in the field of precision farming. These companies provide modern equipment and software, which help farmers in monitoring and analyzing the farm.
5. Precision farming technologies currently used in India include GPS-enabled automatic tractors, machinery, GIS technology, drones, crop sensors, soil sensors, weather forecasting, and modern mobile applications etc. However, the high initial cost is proving to be a deterrent for small and marginal farmers.
Need for Precision agriculture in Indian Farmers
1. The introduction and adoption of Precision farming and modern technology in Indian agriculture is imperative to meet the huge food requirement of 480 million tons by 2050 and to deal with various challenges like climate change, drought, and flood.
2. The global food system is facing formidable challenges and it will increase further in the next 40 years. Declining total productivity, depletion of natural resources, stagnant agricultural practices, lack of eco-regional perspective, declining and degraded land holdings, trade liberalization on agriculture, limited employment opportunities in the non-agricultural sector and global climate change have become major concerns for agricultural development and growth. Therefore, the adoption of newly emerging technology is seen as a key to increasing agricultural productivity in the future. Various institutes and organizations are providing training and technical assistance to farmers.
3. Many private companies and startups are also active in the field of precision farming. These companies provide modern equipment and software that help farmers monitor and analyze the crop.
4. Precision farming technologies currently used in India include GPS-enabled automatic tractors, machinery, drones, crop sensors, soil sensors, weather forecasting, etc. However, the high initial cost is proving to be a deterrent for small and marginal farmers.
Success stories of precision agriculture in Indian farmers
Here are some success stories of Precision agriculture in Indian farmers…

1. Gujarat - Drip Irrigation & Precision Farming
Farmer: Rajendra Parmar (Gujarat)
Story: Rajendra Parmar, a farmer from Gujarat, adopted drip irrigation along with precision agriculture technology to monitor soil moisture levels. Using sensors to detect the water requirements of his crops, he was able to control the irrigation system more efficiently, reducing water wastage. By applying the right amount of water and fertilizers, Rajendra was able to grow crops such as cotton, groundnut, and sugarcane more effectively. This approach led to better water and fertilizer usage, resulting in a 30-40% increase in his overall crop yield and improved productivity
2. Madhya Pradesh - Drones for Pest Control
- Farmer: Ajeet Kumar (Madhya Pradesh)
- Story: Ajeet Kumar, a farmer from Madhya Pradesh, uses drones to spray pesticides over his fields. The drones helped him target specific areas where pests were present, ensuring that pesticides were applied accurately and at optimal levels. This reduced pesticide usage and improved crop health. Ajeet reported a 20% reduction in pesticides.
3.Uttar Pradesh - Precision Irrigation for Wheat Farming
- Farmer: Vinod Kumar (Uttar Pradesh)
- Story: Vinod Kumar, a wheat farmer in Uttar Pradesh, adopted precision irrigation systems that used soil moisture sensors to ensure that his fields received the right amount of water. By integrating technology with his irrigation system, Vinod saved water, minimized wastage, and improved the 15-20% crop yield
4. Maharashtra - Precision Agriculture with Satellite Data
- Farmers: A group of farmers (Maharashtra)
- Story: In Maharashtra, a group of farmers partnered with a company that provided satellite-based data for precision farming. The data helped them monitor crop growth, detect disease, and predict weather patterns. This enabled the farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. farmers improved overall yields by 30% and reduced input costs by around 20%.
5. Andhra Pradesh - Smart Farming with Mobile Apps
- Farmer: Ravi Kumar (Andhra Pradesh)
- Story: Ravi Kumar, a farmer from Andhra Pradesh, used mobile apps to access real-time information on weather, soil health, and pest management. The app provided him with recommendations on when to irrigate, fertilize, and harvest his crops based on accurate data. Ravi’s productivity increased by 20%
conclusion
Today there is a need to provide pure floss to every farmer so that maximum production can be taken using minimum resources. At present both technologies are being used a lot. Still, apart from this, proper use of crop sensing, saddle sensing, automatic machinery, smart irrigation, and weather sensors is also essential to increase production in agriculture.
People also ask
What is precision agriculture?
Precision agriculture involves using advanced technologies like GPS, GIS, Drones IoT, and data analytics to optimize crop yields and resource management.
What are the benefits of precision farming for Indian farmers?
Precision farming helps Indian farmers increase crop yields by up to 30% and reduce water usage by 20-25%, leading to higher profitability and sustainable practices.
Which technologies are driving precision agriculture in India?
GIS, GPS, satellite imagery, automation, drones, and IoT devices are driving precision agriculture in India, enhancing sustainability, productivity and efficiency in farming.
What challenges do Indian farmers face in adopting precision agriculture?
Challenges include small land holdings, high initial investment costs, lack of technical knowledge, and limited access to advanced technologies.
How is the Indian government supporting precision agriculture?
The Indian government has launched initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) to improve farm productivity and ensure better utilization of resources, promoting precision agriculture practices.
References
National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGPA)
Government of India.
LinkDigital Agriculture Mission (2021-2025)
Department of Agriculture, Government of India.
LinkSub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India.
LinkAgri-Stack Initiative
NITI Aayog.
LinkPrecision Agriculture Adoption in India
Agri-Tech India.
LinkChallenges in Precision Farming in India
Agricultural Economics Research Review.
LinkDrones and IoT in Precision Agriculture
ICAR.
LinkGlobal Trends in Precision Agriculture
IFPRI.
Link



