
Introduction: Seeds and Sowing Methods in Agronomy—Fundamentals of Agronomy 3rd part
Understanding the concept of Seeds and Sowing Methods in Agronomy is the first step toward becoming a successful agriculture student or professional. This topic not only builds the basics of crop establishment but also helps you master key concepts that are frequently asked in competitive agriculture exams.
In this visual-based section, you’ll explore:
Topic covers
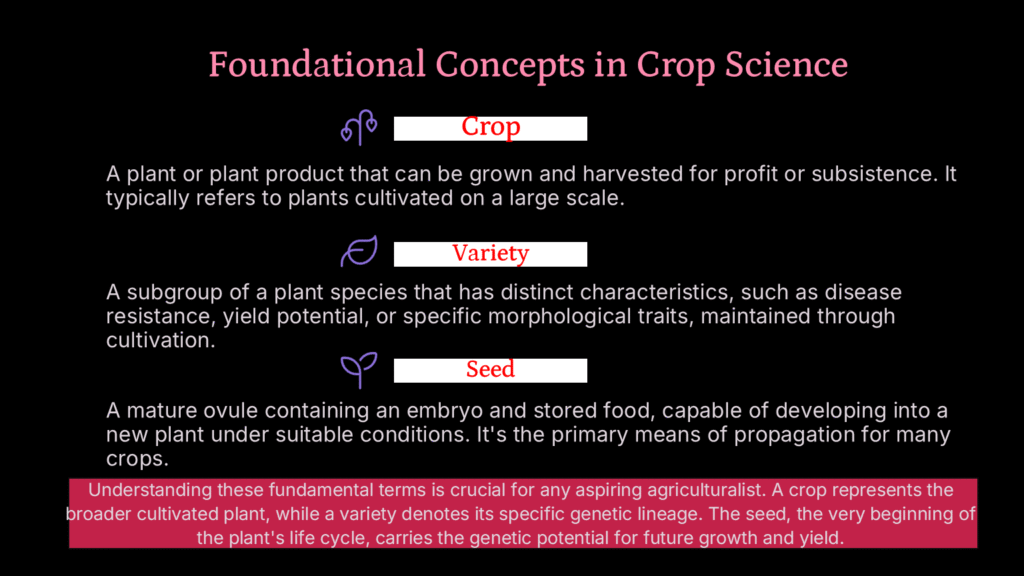
What are crop, variety, and seed
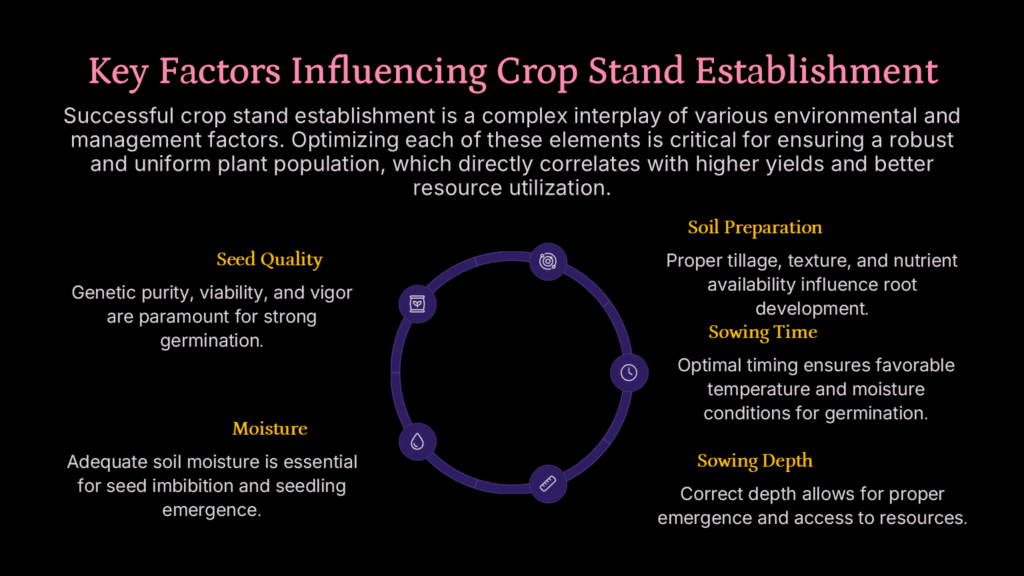
What factors affect crop stand establishment
Various methods of sowing are used by farmers
Each slide is designed with infographics, tables, and clear explanations to ensure that even beginners can understand it easily. Whether you’re a B.Sc. Agriculture student or preparing for an agriculture job exam, this content follows the 6th Dean Committee syllabus and offers a systematic way to learn, just like a classroom!
Scroll down through the slide-by-slide visuals and summaries to gain a crystal-clear understanding.
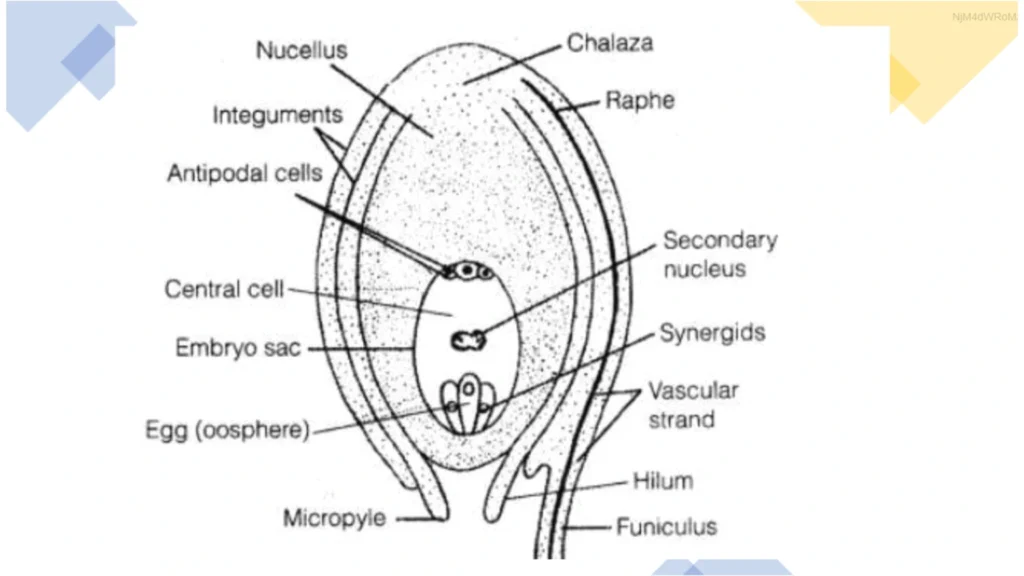
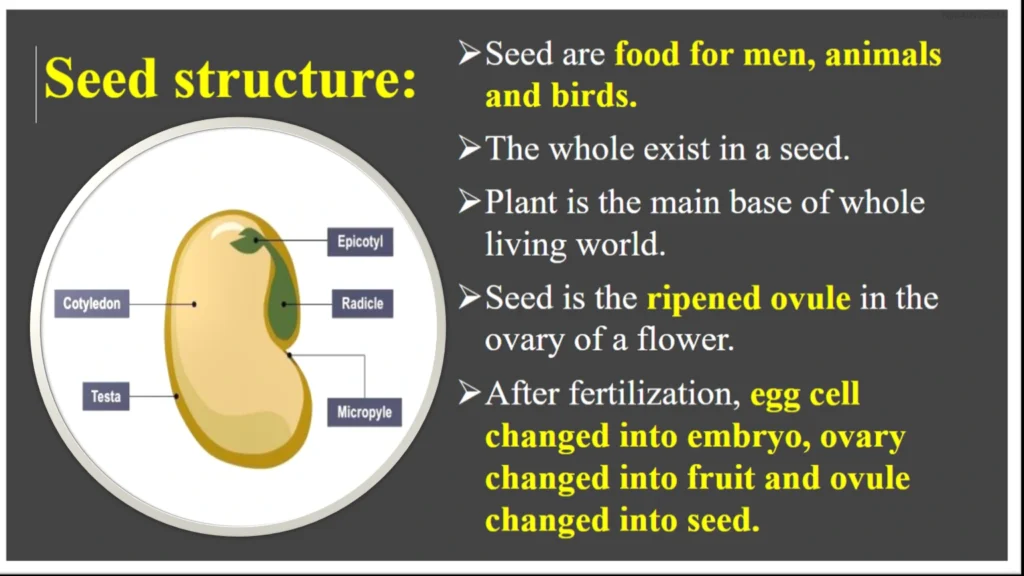
What is seed

definition of seed

structure of a seed
concepts of crop, variety and seed
Factor effecting of seed
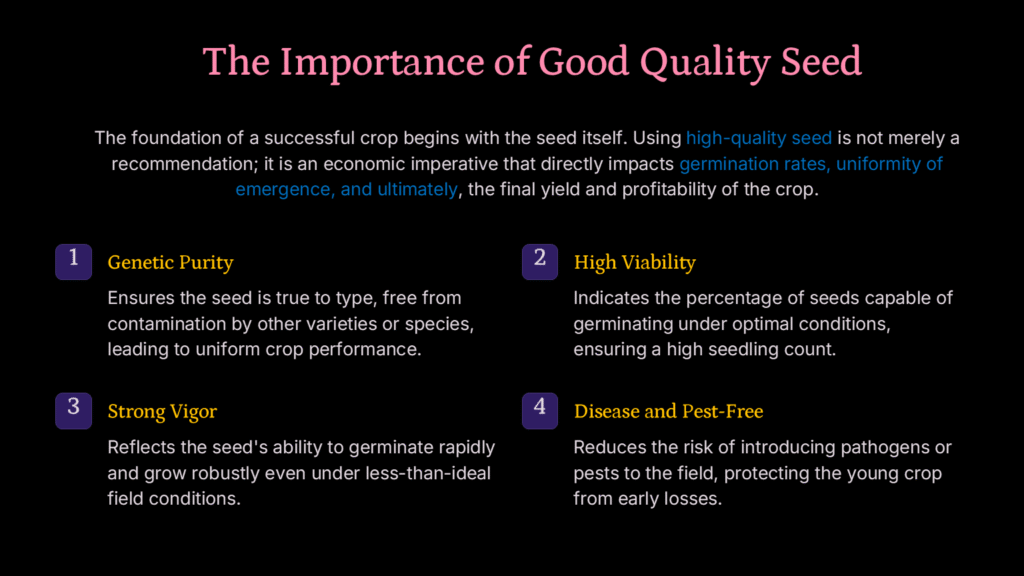
Importance of good quality seed
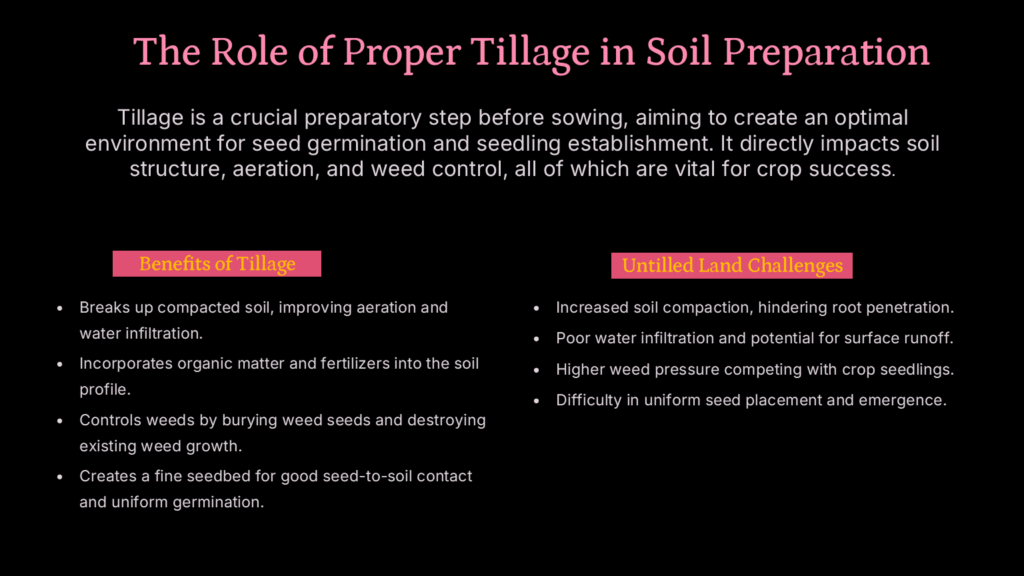
Role of tillage in soil preparation
Impact of sowing time on crop yield

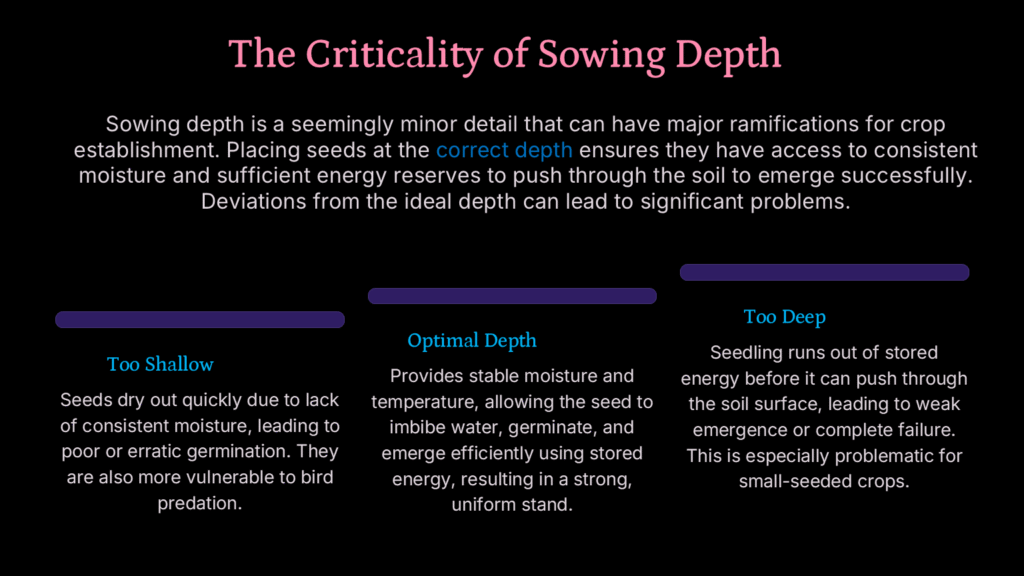
Impact of sowing depth on yield
What is sowing

Feature of perfect sowing

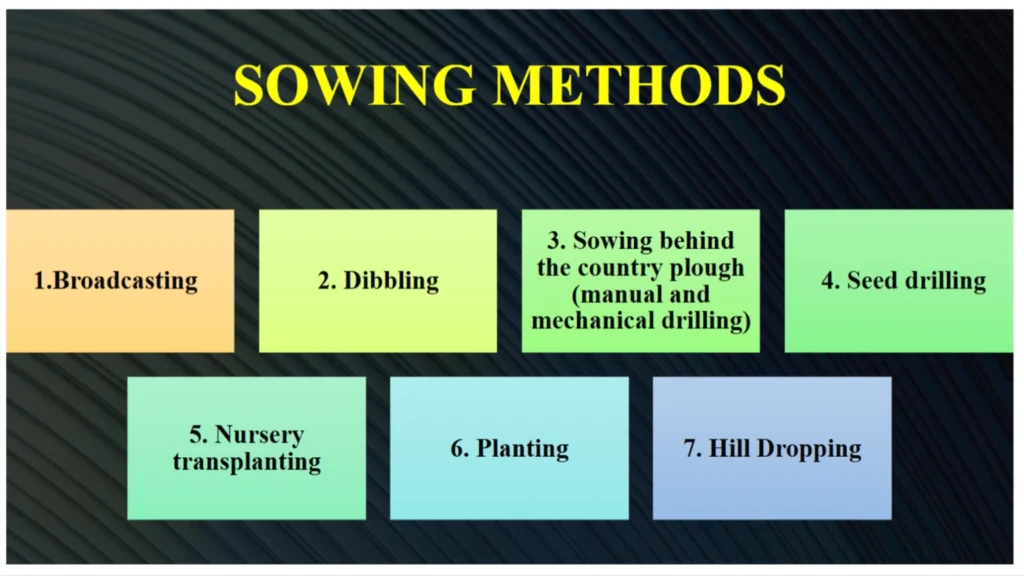
Sowing methods
Sowing method- broadcasting

Disadvantages of broadcasting

Sowing method- dibbling

Sowing method- drilling

Sowing method transplanting

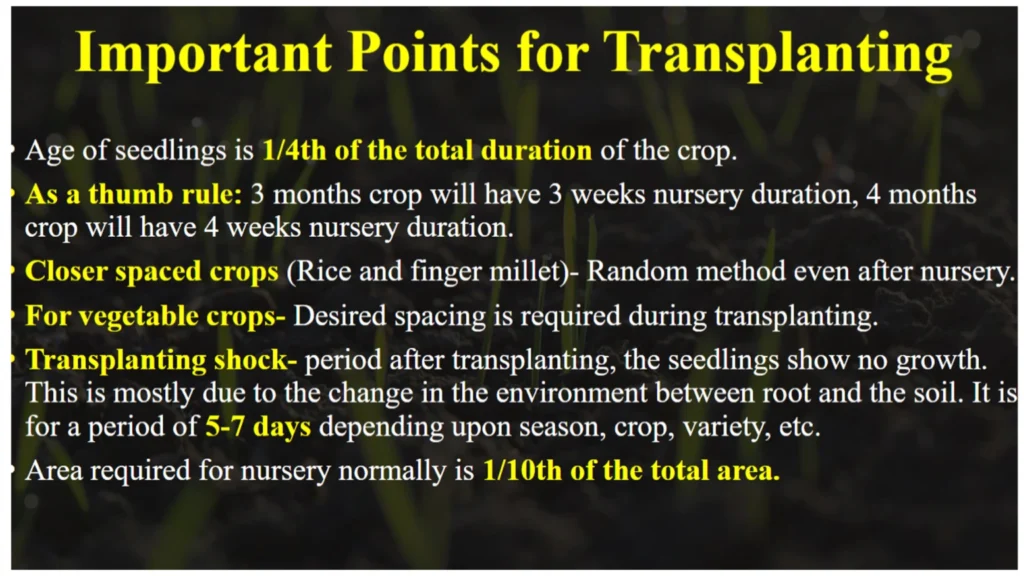
Important points of transplanting
🌾5 Previous Year Questions (AFO, NABARD) in seed and sowing topic
1. Which of the following is not a prerequisite for sowing? (ExamUps, 2024)
A. Good tilth
B. Optimal soil moisture at sowing depth
C. High soil temperature
D. Manures and fertilizers
📝 Additional Information
A. Good tilth → This means the soil is loose, crumbly, and aerated – ideal for seed germination. This is essential.
B. Optimal soil moisture → Moisture at sowing depth is crucial so seeds can absorb water to start germination.
C. High soil temperature → While temperature matters, high temperature is not a general requirement. Some crops need moderate or cool soil. Hence, this is not always needed.
D. Manures and fertilizers → These supply nutrients for seedling development, so they are a regular prerequisite.
2. Which of the following is not a method of artificial sowing? (Studocu, 2023)
A. Broadcasting
B. Dibbling
C. Transplanting
D. Seed drilling
📝 Additional Information
A. Broadcasting → Seeds are scattered randomly on the field – it’s an artificial method.
B. Dibbling → Seeds are placed in holes at proper spacing – also artificial.
C. Transplanting → This involves raising seedlings separately (nursery) and shifting them to the main field – not direct sowing.
D. Seed drilling → Seeds are placed in lines using tools – artificial sowing.
✅ Why C is correct: Transplanting is an establishment method, not a sowing method.
3. What is the seed rate of hybrid rice? (AFO Exam, 2023)
A. 15 kg/ha
B. 25 kg/ha
C. 60 kg/ha
D. None of these
📝 Additional Information
A. 15 kg/ha → This is used for line sowing of some fine cereals, not hybrid rice.
B. 25 kg/ha → Close, but still not enough for hybrid rice.
C. 60 kg/ha → Correct seed rate for hybrid rice under transplanting conditions.
D. None of these → Incorrect, since C is the right value.
✅ Why C is correct: Hybrid rice requires more seed due to its specific plant population needs.
4. Which method of sowing involves placing seeds in small pits or furrows? (AFO Exam, 2024)
A. Broadcasting
B. Dibbling
C. Transplanting
D. Seed drilling
📝 Additional Information
A. Broadcasting → No pits, just scattered over surface.
B. Dibbling → Seeds placed one by one into pits/furrows – ensures spacing.
C. Transplanting → Deals with seedlings, not seeds.
D. Drilling → Line-wise sowing using machines.
✅ Why B is correct: Dibbling is the only method that uses manual hole/pit placement.
5. What issue can arise if seeds exhibit dormancy? (NABARD)
A. Rapid germination
B. Uniform crop stand
C. Delayed or failed germination
D. Enhanced seed vigour
📝 Additional Information
A. Rapid germination → Opposite of dormancy.
B. Uniform stand → Not possible if seeds germinate unevenly.
C. Delayed/failure → Dormant seeds won’t germinate even if conditions are favorable.
D. Enhanced vigor → Dormancy reduces effective seedling emergence.
✅ Why C is correct: Dormant seeds need treatment or time to become active – a big issue in sowing.
conclusion: Seeds and Sowing Methods in Agronomy
Understanding the concepts of seeds and sowing is not just fundamental for academic success in the B.Sc. Agriculture is also essential for anyone preparing for competitive agricultural exams. From the selection of good-quality seeds to the correct sowing method, every step plays a vital role in ensuring a better crop stand and yield. The detailed explanation provided through visual slides, simple definitions, and previous years’ questions helps nearly strengthen your basics.
If you found this content helpful and want to explore the full Fundamentals of Agronomy subject in a structured, visual, and exam-focused format —
👉 Click here to go to the main Agronomy Page, where you’ll get all parts, notes, and PYQs in one place.
Stay consistent, keep revising, and grow with AgriGramodaya — your trusted guide for agriculture learning.
Click to Join Our Free WhatsApp Group for Agriculture Updates!
Get daily updates, free study material, and the latest schemes, and connect with other agriculture students and farmers.
After bsc agriculture exam (New Syllabus )
Latest Syllabus | Download Here |
IBPS Agriculture Filed Officer | |
NABARD GRADE A | |
Food Corporation of India (FCI) | |
RAEO | |
RHEO | |
Food Inspector | |
IFFCO AGT | |
MP PAT | |
UPSSSC AGTA |
Read more fundamentals of agronomy Topics
Read B.Sc. agriculture syllabus and notes
Important message
📥 Want This PPT for Personal Use?
If you want this full presentation in PPT format for offline study or classroom use, feel free to message me personally on WhatsApp.
I’ll be happy to share it with you!
📲 WhatsApp 9343512089
📝 Note: This is for educational purposes only. Please don’t redistribute without permission.
Latest post
👉Top 100 Crop Improvement in Rabi Crops MCQs + Fill in Blanks + One Liners (Exam Special)
Crop improvement in rabi crops MCQs is one of the...
Read More👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More80+ Post Harvest Management MCQs, Fill in the Blanks & Short Questions (Exam-Oriented)
Post harvest management is one of the most important units...
Read MoreR.S. Singh Plant Diseases Book PDF: The “Gift” for Plant Pathology Students
Table of Contents If you are a BSc Agriculture student,...
Read More🙋♂️ About the Author
Khumesh, a BSc Agriculture student and founder of AgriGramodaya.com, is on a mission to make “Fundamentals of Agronomy” the easiest and most accessible subject for students across India.
Having personally faced the challenge of finding clear, structured, and visual content for Agronomy, he decided to build a complete one-page resource, breaking down the full syllabus into simple parts — supported by PPTs, summary notes, previous-year MCQs, and exam-oriented insights.
Every part of this subject is designed to help students from zero to advanced level, whether you’re preparing for semester exams or agriculture job exams.
📚 Learn visually. Revise smartly. Succeed confidently — only on AgriGramodaya.




