Field Crops and their Classification PPT
Welcome to the second part of our “Fundamentals of Agronomy” series on AgriGramodaya, where we simplify agricultural concepts for students, competitive exam aspirants, and curious learners. This page focuses on Field Crops and Their Classification, one of the most important foundational topics in Agronomy.
The purpose of this blog is to provide you with clear, beginner-friendly, and exam-oriented knowledge about:
What are field crops?
How are field crops classified based on various criteria?
Why is classification important in agronomy and crop planning?
We have structured the content in a slide-wise format, breaking the full topic into easy-to-understand sections. Each part is supported by definitions, examples, and simple explanations to help you grasp the core idea without confusion.
In addition to the theory, we have also included:
✅ A clear PPT slide structure for revision
✅ Well-explained previous years’ MCQs from real agriculture job exams
✅ Practical classification types to support your semester preparation and competitive exams like ICAR, FCI, NABARD, AFO, RAEO, and others.
🔍 My aim with this series is not just to help you study — but to make you confident, help you build strong fundamentals, and guide you like a fellow student who knows your struggle.
Let’s dive into the world of field crops and master this topic step-by-step. 🌱
Topics cover
PART 2: Field Crops and Classification
What are field crops?
Classification of Field Crops (based on season, use, lifecycle)
Importance of Different Crops in Indian Agriculture
Introduction of field crops

importance of field crops

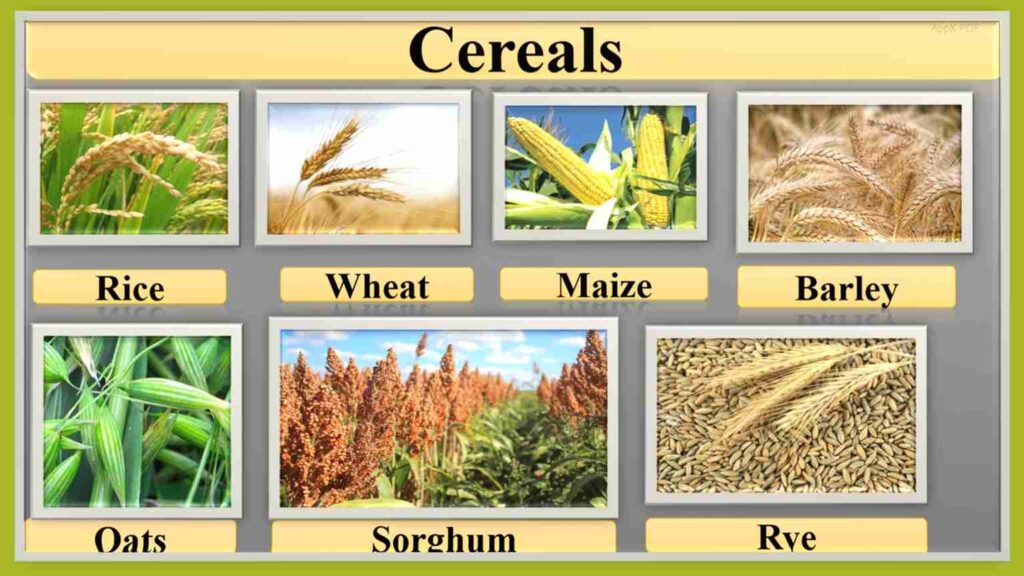
cereal crops examples
millets crops examples
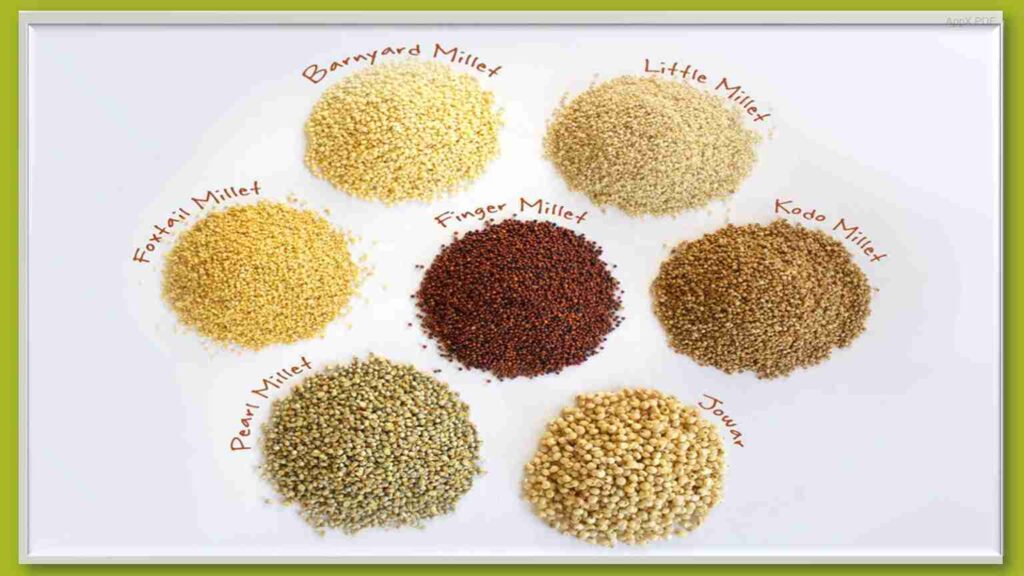

field crop classification based on season

field crop classification based on life cycle

field crop classification based on use

field crop classification based on botnical classification

field crop classification based on leaf type

field crop classification based oneconomic purpose

field crop classification based on special crops


10 Previous Year Questions from Field Crops and their Classification (Part 2)—Asked in ICAR, AFO, etc. exams
1. Which of the following crops is classified as a kharif crop in India? (Asked in: ICAR AIEEA UG, 2019)
A. Wheat
B. Barley
C. Rice
D. Mustard
📝 Additional Information
Kharif crops are sown at the beginning of the monsoon (June–July) and harvested at the end (September–October).
Rice is a typical kharif crop because it needs high temperature (above 25°C) and abundant water during its growth period, which the monsoon provides.
Wheat and Barley are rabi crops, grown in winter and harvested in spring (sown in October–November).
Mustard is also a rabi crop and needs a cooler climate.
Summary: Rice fits the climate and sowing/harvesting timeline of kharif crops, making it the correct choice.
2. Which of the following is a commercial crop? (Asked in: NABARD Grade A Prelims, 2020)
A. Wheat
B. Cotton
C. Rice
D. Maize
📝 Additional Information
Commercial crops are grown mainly for sale rather than for personal consumption.
Cotton is a commercial crop because it’s sold to textile industries.
Wheat, rice, and maize are food crops, primarily grown for consumption.
Cotton also needs more investment and is sold in the market for profit.
🟩 So, cotton is classified as a commercial crop, unlike food grains grown for sustenance.
3. Which of the following is a cereal crop? (Asked in: ICAR AIEEA PG, 2021)
A. Chickpea
B. Groundnut
C. Pearl millet
D. Soybean
📝 Additional Information
Cereal crops belong to the grass family (Poaceae) and produce grains.
Pearl millet (Bajra) is a cereal crop grown in arid regions.
Chickpea is a pulse, Groundnut is an oilseed, and Soybean is both oilseed and legume.
🟩 Only Pearl millet is a cereal crop among the options.
4. Which of the following is a legume crop? (Asked in: ASRB NET, 2022)
A. Maize
B. Sugarcane
C. Lentil
D. Cotton
📝 Additional Information
Legumes belong to the family Fabaceae and fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Lentil (Masoor) is a pulse/legume rich in protein.
Maize is a cereal, sugarcane is a cash crop, and cotton is a commercial crop.
🟩 Lentil is the correct answer because it is a classic leguminous crop used to improve soil fertility.
5. Which crop is classified as a plantation crop? (Asked in: UPSC Agriculture Optional, 2021)
A. Jute
B. Coconut
C. Sorghum
D. Barley
📝 Additional Information
Plantation crops are grown on large estates and are long-duration crops.
Coconut trees are perennial and grown mainly in coastal areas for commercial use.
Jute is a fibre crop, Sorghum and Barley are cereals.
🟩 Coconut fits the plantation crop category due to its perennial nature and market value.
6. Pulses are a rich source of which nutrient? (Asked in: FCI Assistant Grade III, 2020)
A. Fats
B. Carbohydrates
C. Proteins
D. Vitamins
📝 Additional Information
Pulses like chickpea, lentil, and moong dal are protein-rich foods.
They help build body tissues and are important in vegetarian diets.
Carbohydrates are found in cereals like rice, wheat.
Fats are found in oils, nuts; vitamins come from fruits and vegetables.
🟩 Proteins are the primary nutrient found in pulses.
7. Which crop is grown in Zaid season? (Asked in: SSC GD Constable, 2021)
A. Watermelon
B. Wheat
C. Rice
D. Mustard
📝 Additional Information
Zaid crops are grown between rabi and kharif, i.e., from March to June.
Watermelon needs a warm climate and short duration.
Wheat and mustard are rabi crops.
Rice is mainly a kharif crop.
🟩 Watermelon is a typical Zaid crop due to its growing season.
8. Which one of the following is a fibrecrop? ?(Asked in: ICAR JRF, 2018
A. Sugarcane
B. Cotton
C. Groundnut
D. Chickpea
📝 Additional Information
Fibre crops are grown for their fibres used in textiles.
Cotton is the leading fibre crop in India.
Sugarcane is grown for juice, groundnut for oil, and chickpea for pulses.
🟩 Cotton is a fibre crop because its lint is spun into thread and cloth.
9. Sorghum is a: (Based on economic use) (Asked in: IBPS AFO, 2019)
A. Fibre crop
B. Food crop
C. Plantation crop
D. Oilseed crop
📝 Additional Information
Sorghum (Jowar) is a cereal and used as food grain, especially in dry regions.
It is also used for fodder.
It’s not used for fibre, plantation, or oil production.
🟩 Sorghum is classified as a food crop due to its edible grain.
10. Which of the following is a Rabi crop? (Agriculture Supervisor Exam, Rajasthan, 2022)
A. Moong
B. Groundnut
C. Mustard
D. Cotton
Conclusion: Field Crops and their Classification
Understanding the classification of field crops and their classification is essential for anyone entering the world of agriculture — whether you’re a BSc Agriculture student or preparing for competitive exams. With a proper grasp of this topic, you can make better decisions related to crop selection, season planning, and land management.
We hope this visual and easy-to-follow content has made this topic simple and interesting for you.
📌 But this is just one part of the full Agronomy syllabus!
If you want to explore all topics of Fundamentals of Agronomy — explained in a similar student-friendly and visually rich format — then don’t miss our main Agronomy resource page.
🎯 Click below to access the complete topic-wise content, MCQs, and presentations designed to help you master agronomy step by step:
👉 [Go to the Main Agronomy Page Now]
Click to Join Our Free WhatsApp Group for Agriculture Updates!
Get daily updates, free study material, and the latest schemes, and connect with other agriculture students and farmers.
After bsc agriculture exam (New Syllabus )
Latest Syllabus | Download Here |
IBPS Agriculture Filed Officer | |
NABARD GRADE A | |
Food Corporation of India (FCI) | |
RAEO | |
RHEO | |
Food Inspector | |
IFFCO AGT | |
MP PAT | |
UPSSSC AGTA |
Read B.Sc. agriculture syllabus and notes
Read latest posts
👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More80+ Post Harvest Management MCQs, Fill in the Blanks & Short Questions (Exam-Oriented)
Post harvest management is one of the most important units...
Read MoreR.S. Singh Plant Diseases Book PDF: The “Gift” for Plant Pathology Students
Table of Contents If you are a BSc Agriculture student,...
Read MoreNemraj Sunda 15th Edition PDF Download Free : Is It Still the Ultimate Guide for Agri-Exams?
Table of Contents If you have ever stepped into an...
Read More🙋♂️ About the Author
Khumesh, a BSc Agriculture student and founder of AgriGramodaya.com, is on a mission to make “Fundamentals of Agronomy” the easiest and most accessible subject for students across India.
Having personally faced the challenge of finding clear, structured, and visual content for Agronomy, he decided to build a complete one-page resource, breaking down the full syllabus into simple parts — supported by PPTs, summary notes, previous-year MCQs, and exam-oriented insights.
Every part of this subject is designed to help students from zero to advanced level, whether you’re preparing for semester exams or agriculture job exams.
📚 Learn visually. Revise smartly. Succeed confidently — only on AgriGramodaya.




