Download BSc agriculture 6th semester Notes in hindi and english
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in Hindi.
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | Hindi Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in English
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
BSc Agriculture 6th Semester notes and Syllabus
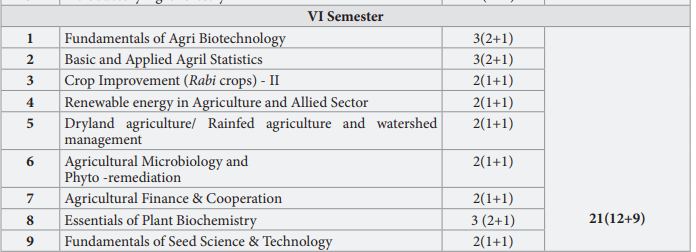
Rainfed Agriculture and Watershed Management – (New)
Theory
Rainfed agriculture: Introduction, types, History of rainfed agriculture & watershed in India; Problems and prospects of rainfed agriculture in India ; Soil and climatic conditions prevalent in rainfed areas; Drought: types, effect of water deficit on physio- morphological characteristics of the plants, Mechanism of crop adaptation under moisture deficit condition; Water harvesting: importance, its techniques, Efficient utilization of water through soil and crop management practices,Management of crops in rainfed areas, Contingent crop planning for aberrant weather conditions, Concept, objective, principles and components of watershed management, factors affecting watershed management.
Practical
studies on climate classification, studies on rainfall patterns in rainfed areas of the country and patterns of onset and withdrawal of monsoons. Studies on cropping patterns of different dryland areas in the country and demarcation of dry land area on map of India. Interpretation of meteorological data and scheduling of supplemental irrigation on the basis of evapotranspiration demand of crops. Critical analysis of rainfall and possible drought period in the country, effective rainfall and its calculation. Studies on cultural practices viz; mulching, plant density, depth of sowing, thinning and leaf removal for mitigating moisture stress. Characterization and delineation of model watershed. Field demonstration on soil & moisture conservation measures. Field demonstration on construction of water harvesting structures. Visit to rainfed research station/watershed.
Protected Cultivation and Secondary Agriculture
Theory
Green house technology: Introduction, Types of Green Houses; Plant response to Green house environment, Planning and design of greenhouses, Design criteria of green house for cooling and heating purposes. Green house equipment, materials of construction for traditional and low-cost green houses. Irrigation systems used in greenhouses, typical applications, passive solar green houses, hot air greenhouse heating systems, and greenhouse drying. Cost estimation and economic analysis. Important Engineering properties such as physical, thermal and aero & hydrodynamic properties of cereals, pulses and oilseed, and their application in PHT equipment design and operation. Drying and dehydration; moisture measurement, EMC, drying theory, various drying methods, commercial grain dryer (deep bed dryer, flatbed dryer, tray dryer, fluidized bed dryer, recirculatory dryer and solar dryer). Material handling equipment; conveyors and elevators, their principle, working and selection.
Practical
Study of different types of greenhouses based on shape. Determine the rate of air exchange in an active summer-winter cooling system. Determination of drying rate of agricultural products inside greenhouse. Study of greenhouse types of equipment. Visit various Post Harvest Laboratories. Determination of Moisture content of various grains by oven drying & infrared moisture methods. Determination of engineering properties (shape and size, bulk density and porosity of biomaterials). Determination of Moisture content of various grains by moisture meter. Field visit to the seed processing plant.
Diseases of Field & Horticultural Crops & their Management-II
Theory
Symptoms, etiology, disease cycle and management of following diseases:Field Crops: Wheat: rusts, loose smut, karnal bunt, powdery mildew, alternaria blight, and ear cockle; Sugarcane: red rot, smut, wilt, grassy shoot, ratoon stunting and Pokkah Boeng;Sunflower: Sclerotinia stem rot and Alternaria blight; Mustard: Alternaria blight, white rust, downy mildew and Sclerotinia stem rot; Gram: wilt, grey mould and Ascochyta blight; Lentil: rust and wilt;Cotton: anthracnose, vascular wilt, and black arm;Pea: downy mildew, powdery mildew and rustHorticultural Crops: Mango: anthracnose, malformation, bacterial blight and powdery mildew;Citrus: canker and gummosis;Grape vine: downy mildew, Powdery mildew and anthracnose;Apple: scab, powdery mildew, fire blight and crown gall;Peach: leaf curl Strawberry: leaf spot Potato: early and late blight, black scurf, leaf roll, and mosaicCucurbits: downy mildew, powdery mildew, wilt;Onion and garlic: purple blotch, and Stemphylium blight;Chillies: anthracnose and fruit rot, wilt and leaf curl;Turmeric: leaf spot Coriander: stem gallMarigold: Botrytis blight; Rose: dieback, powdery mildew and black leaf spot.
Practical
Identification and histopathological studies of selected diseases of field and horticultural crops covered in theory. Field visits for the diagnosis of field problems. Collection and preservation of plant-diseased specimens for herbarium.Note: Students should submit 50 pressed and well-mounted specimens
Post-harvest Management and Value Addition of Fruits and Vegetables
Theory
Importance of fruits and vegetables, extent and possible causes of post-harvest losses; Pre-harvest factors affecting postharvest quality, maturity, ripening and changes occurring during ripening; Respiration and factors affecting respiration rate; Role of ethylene; Post-harvest disease and disorders; Heat, chilling and freezing injury; Harvesting and field handling; Storage (ZECC, cold storage, CA, MA, and hypobaric); Value addition concept; Principles and methods of preservation; Intermediate moisture food- Jam, jelly, marmalade, preserve, candy – Concepts and Standards; Fermented and non-fermented beverages. Tomato products- Concepts and Standards; Drying/ Dehydration of fruits and vegetables – Concept and methods, osmotic drying. Canning -– Concepts and Standards, packaging of products.
Practical
Applications of different types of packaging containers for shelf life extension. Effect of temperature on shelf life and quality of produce. Demonstration of chilling and freezing injury in vegetables and fruits. Extraction and preservation of pulps and juices. Preparation of jam, jelly, RTS, nectar, squash, osmotically dried products, fruit bar and candy and tomato products, and canned products. Quality evaluation of products — physico-chemical and sensory. Visit to processing unit/ industry.
Management of Beneficial Insects
Theory
Importance of beneficial Insects, Beekeeping, pollinating plant and their cycle, bee biology, commercial methods of rearing, equipment used, seasonal management, bee enemies and disease. Bee pasturage, bee foraging and communication. Insect pests and diseases of honey bee. Types of silkworm, voltinism and biology of silkworm. Mulberry cultivation, mulberry varieties and methods of harvesting and preservation of leaves. Rearing, mounting and harvesting of cocoons. Pest and diseases of silkworm, management, rearing appliances of mulberry silkworm and methods of disinfection. Species of lac insect, morphology, biology, host plant, lac production – seed lac, button lac, shellac, lac- products. Identification of major parasitoids and predators commonly being used in biological control. Insect orders bearing predators and parasitoids used in pest control and their mass multiplication techniques. Important species of pollinators, weed killers and scavengers with their importance.
Practical
Honey bee species, castes of bees. Beekeeping appliances and seasonal management, bee enemies and disease. Bee pasturage, bee foraging and communication. Types of silkworm, voltinism and biology of silkworm. Mulberry cultivation, mulberry varieties and methods of harvesting and preservation of leaves. Species of lac insect, host plant identification. Identification of other important pollinators, weed killers and scavengers. Visit to research and training institutions devoted to beekeeping, sericulture, lac culture and natural enemies.
Crop Improvement – II (Rabi)
Theory
Centres of origin, distribution of species, wild relatives in different cereals; pulses; oilseeds; fodder crops and cash crops; vegetable and horticultural crops; Plant genetic resources, its utilization and conservation; Floral biology, the study of the genetics of qualitative and quantitative characters; Important concepts of breeding self-pollinated, cross-pollinated and vegetatively propagated crops; Major breeding objectives and procedures including conventional and modern innovative approaches for development of hybrids and varieties for yield, adaptability, stability, abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and quality (physical, chemical, nutritional); Seed production technology in self pollinated, cross pollinated and vegetatively propagated crops. Hybrid seed production technology of rabi crops. Ideotype concept and climate resilient crop varieties for the future.
Practical
Emasculation and hybridization techniques in different crop species namely Wheat, Oat, Barley, Chickpea, Lentil, Field pea, Rapeseed Mustard, Sunflower, Potato, and Berseem. Sugarcane, Cowpea; Handling of germplasm and segregating populations by different methods like pedigree, bulk and single seed descent methods; Study of field techniques for seed production and hybrid seeds production in Rabi crops; Estimation of heterosis, inbreeding depression and heritability; Layout of field experiments; Study of quality characters, study of donor parents for different characters; Visit to seed production plots; Visit to AICRP plots of different field crops.
.Practical Crop Production-II (Rabi Crops)
Theory
Centres of origin, distribution of species, wild relatives in different cereals; pulses; oilseeds; fodder crops and cash crops; vegetable and horticultural crops; Plant genetic resources, its utilization and conservation; Floral biology, the study of the genetics of qualitative and quantitative characters; Important concepts of breeding self-pollinated, cross pollinated and vegetatively propagated crops; Major breeding objectives and procedures including conventional and modern innovative approaches for the development of hybrids and varieties for yield, adaptability, stability, abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and quality (physical, chemical, nutritional); Seed production technology in self-pollinated, cross pollinated and vegetatively propagated crops. Hybrid seed production technology of rabi crops. Ideotype concept and climate resilient crop varieties for the future.
Practical
Emasculation and hybridization techniques in different crop species namely Wheat, Oat, Barley, Chickpea, Lentil, Field pea, Rapeseed Mustard, Sunflower, Potato, Berseem. Sugarcane, Cowpea; Handling of germplasm and segregating populations by different methods like pedigree, bulk and single seed decent methods; Study of field techniques for seed production and hybrid seeds production in Rabi crops; Estimation of heterosis, inbreeding depression and heritability; Layout of field experiments; Study of quality characters, study of donor parents for different characters; Visit to seed production plots; Visit to AICRP plots of different field crops.Practical Crop Production-II (Rabi Crops)Credit hours: 2(0+2)Practical Crop planning, raising field crops in multiple cropping systems: Field preparation, seed, treatment, nursery raising, sowing, nutrient, water and weed management and management of insect-pests diseases of crops, harvesting, threshing, drying winnowing, storage and marketing of produce. The emphasis will be given to seed production, mechanization, resource conservation and integrated nutrient, insect-pest and disease management technologies. Preparation of balance sheet including cost of cultivation, net returns per student as well as per team of 8-10 students.
Principles of Organic Farming
Theory
Organic farming, principles and its scope in India; Initiatives are taken by Government (central/state), NGOs and other organizations for the promotion of organic agriculture; Organic ecosystem and their concepts; Organic nutrient resources and its fortification; Restrictions to nutrient use in organic farming; Choice of crops and varieties in organic farming; Fundamentals of insect, pest, disease and weed management under the organic mode of production; Operational structure of NPOP; Certification process and standards of organic farming; Processing, levelling, economic considerations and viability, marketing and export potential of organic products.
Practical
Visit organic farms to study the various components and their utilization; Preparation of enriched compost, vermicompost, bio-fertilizers/bio-inoculants and their quality analysis; Indigenous technology knowledge (ITK) for nutrient, insect, pest disease and weed management; Cost of the organic production system; Post-harvest management; Quality aspect, grading, packaging and handling. Farm Management,
BSc agriculture 6th semester Notes and important books
Other semester syllabus and notes
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Related post-
👉Top 100 Crop Improvement in Rabi Crops MCQs + Fill in Blanks + One Liners (Exam Special)
Crop improvement in rabi crops MCQs is one of the...
Read More👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More80+ Post Harvest Management MCQs, Fill in the Blanks & Short Questions (Exam-Oriented)
Post harvest management is one of the most important units...
Read MoreR.S. Singh Plant Diseases Book PDF: The “Gift” for Plant Pathology Students
Table of Contents If you are a BSc Agriculture student,...
Read More





