Download- BSc agriculture 5th semester notes in Hindi and English.
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in Hindi.
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | Hindi Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in English
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
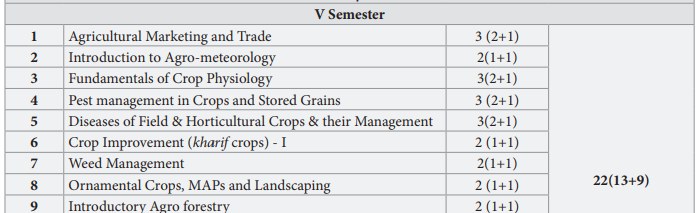
BSc Agriculture 5th Semester notes and Syllabus
Principles of Integrated Pest and Disease Management
Theory
Categories of insect pests and diseases, IPM: Introduction, history, importance, concepts, principles and tools of IPM. Economic importance of insect pests, diseases and pest risk analysis. Methods of detection and diagnosis of insect pests and diseases. Calculation and dynamics of economic injury level and importance of Economic threshold level. Methods of control: Host plant resistance, cultural, mechanical, physical, legislative, biological and chemical control. Ecological management of crop environment. Introduction to conventional pesticides for insect pests and disease management. Surveysurveillance and forecasting of Insect pests and diseases. Development and validation of IPM module. Implementation and impact of IPM (IPM module for Insect pests and disease. Safety issues in pesticide uses. Political, social and legal implications of IPM. Case histories of important IPM programmes.
Practical
Methods of diagnosis and detection of various insect pests, and plant diseases, Methods of insect pests and plant disease measurement, Assessment of crop yield losses, calculations based on economics of IPM, Identification of biocontrol agents, different predators and natural enemies. Mass multiplication of Trichoderma, Pseudomonas, Trichogramma, NPV etc. Identification and nature of damage of important insect pests and diseases and their management. Crop (agro-ecosystem) dynamics of a selected insect pest and diseases. Plan & assess preventive strategies (IPM module) and decision-making. crop monitoring attacked by insects, pests and diseases. Awareness campaign at farmer’s fields.
Manures, Fertilizers and Soil Fertility Management
Theory
Introduction and importance of organic manures, as well as properties and methods of preparation of bulky and concentrated manures. Green/leaf manuring. Integrated nutrient management.Chemical fertilizers: classification, composition and properties of major nitrogenous, phosphatic, potassic fertilizers, secondary & micronutrient fertilizers, Complex fertilizers, nano fertilizers Soil amendments, Fertilizer Storage, Fertilizer Control Order.History of soil fertility and plant nutrition. criteria of essentiality. role, deficiency and toxicity symptoms of essential plant nutrients, Mechanisms of nutrient transport to plants, and factors affecting nutrient availability to plants. Chemistry of soil nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur and micronutrients. Soil fertility evaluation and soil testing. Critical levels of different nutrients in the soil. Forms of nutrients in soil, plant analysis, rapid plant tissue tests. Indicator plants. Methods of fertilizer recommendations to crops. Factor influencing nutrient use efficiency (NUE), methods of application under rainfed and irrigated conditions.
Practical
introduction of analytical instruments and their principles, calibration and applications, Colorimetry and flame photometry. Estimation of available N in soils. Estimation of available P in soils. Estimation of available K. Estimation of available S in soils. Estimation of available Ca and Mg in soils. Estimation of available Zn in soils. Estimation of N in plants. Estimation of P in plants. Estimation of K in plants. Estimation of S in plants.
Pests of Crops and Stored Grains and their Management
Theory
General account on nature and type of damage by different arthropods pests. Scientific name, order, family, host range, distribution, biology and bionomics, nature of damage, and management of major pests and scientific name, order, family, host range, distribution, nature of damage and control practice other important arthropod pests of various field crop, vegetable crop, fruit crop, plantation crops, ornamental crops, narcotics, spices and condiments. Factors affecting losses of stored grain and role of physical, biological, mechanical and chemical factors in deterioration of grain. Insect pests, mites, rodents, birds and microorganisms associated with stored grain and their management. Storage structure and methods of grain storage and fundamental principles of grain store management.
Practical
Identification of different types of damage. Identification and study of life cycle and seasonal history of various insect pests attacking crops and their produce: (a) Field Crops; (b) Vegetable Crops; (c) Fruit Crops; (d) Plantation, gardens, Narcotics, spices & condiments. Identification of insect pests and Mites associated with stored grain. Determination of insect infestation by different methods. Assessment of losses due to insects. Calculations on the doses of insecticides application technique. Fumigation of grain store/godown. Identification of rodents and rodent control operations in godowns. Identification of birds and bird control operations in godowns. Determination of moisture content of grain. Methods of grain sampling under storage conditions. Visit Indian Storage Management and Research Institute, Hapur and Quality Laboratory, Department of Food., Delhi. Visit to nearest FCI godowns.
Diseases of Field & Horticultural Crops & their Management-I
Theory
Symptoms, etiology, disease cycle and management of major diseases of following crops: Field Crops: Rice: blast, brown spot, bacterial blight, sheath blight, false smut, khaira and tungro;Maize: stalk rots, downy mildew, leaf spots; Sorghum: smuts, grain mould and anthracnose, Bajra: downy mildew and ergot; Groundnut: early and late leaf spots, wilt Soybean: Rhizoctonia blight, bacterial spot, seed and seedling rot and mosaic; Pigeonpea: Phytophthora blight, wilt and sterility mosaic; Finger millet: Blast and leaf spot; black & green gram: Cercospora leaf spot and anthracnose, web blight and yellow mosaic; Castor: Phytophthora blight; Tobacco: black shank, black root rot and mosaic. Horticultural Crops: Guava: wilt and anthracnose; Banana: Panama wilt, bacterial wilt, Sigatoka and bunchy top; Papaya: foot rot, leaf curl and mosaic, Pomegranate: bacterial blight; Cruciferous vegetables: Alternaria leaf spot and black rot; Brinjal: Phomopsis blight and fruit rot and Sclerotinia blight; Tomato: damping off, wilt, early and late blight, buck eye rot and leaf curl and mosaic; Okra: Yellow Vein Mosaic; Beans: anthracnose and bacterial blight; Ginger: soft rot; Colocasia: Phytophthora blight; Coconut: wilt and bud rot; Tea: blister blight; Coffee: rust
Practical
Identification and histopathological studies of selected diseases of field and horticultural crops covered in theory. Field visits for the diagnosis of field problems. Collection and preservation of plant diseased specimens for Herbarium; Note: Students should submit 50 pressed and well-mounted specimens.
Crop Improvement – I (Kharif)
Theory
Centers of origin, distribution of species, wild relatives in different cereals; pulses; oilseeds; fibres; fodders and cash crops; vegetable and horticultural crops; Plant genetic resources, its utilization and conservation Floral biology, the study of the genetics of qualitative and quantitative characters; Important concepts of breeding self-pollinated, cross pollinated and vegetative propagated crops; Major breeding objectives and procedures including conventional and modern innovative approaches for the development of hybrids and varieties for yield, adaptability, stability, abiotic and biotic stress tolerance and quality (physical, chemical, nutritional); Seed production technology in self-pollinated, cross pollinated and vegetatively propagated crops. Hybrid seed production technology in Maize, Rice, Sorghum, Pearl millet and Pigeonpea, etc. Ideotype concept and climate resilient crop varieties for the future.
Practical
Emasculation and hybridization techniques in different crop species; viz., Rice, Maize, Sorghum, Pearl Millet, Ragi, Pigeonpea, Urdbean, Mungbean, Soybean, Groundnut, Seasame , Caster, Cotton, Cowpea, Pearl millet and Tobacco. Maintenance breeding of different kharif crops. Handling of germplasm and segregating populations by different methods like pedigree, bulk and single seed decent methods; Study of field techniques for seed production and hybrid seeds production in Kharif crops; Estimation of heterosis, inbreeding depression and heritability; Layout of field experiments; Study of quality characters, donor parents for different characters; Visit to seed production plots; Visit to AICRP plots of different field crops
Entrepreneurship Development and Business Communication
Theory
Concept of Entrepreneur, Entrepreneurship Development, Characteristics of entrepreneurs; Assessment of entrepreneurship skills, SWOT Analysis & achievement motivation, Entrepreneurial behaviour, Government policy and programs and institutions for entrepreneurship development, Entrepreneurial Development Process; Business Leadership Skills; Communication skills for entrepreneurship development, Developing organizational skill, Developing Managerial skills, Problem-solving skill, Achievement motivation; time management; Supply chain management and Total quality management, Project Planning Formulation and report preparation; Opportunities for entrepreneurship and rural entrepreneurship.
Practical
Assessing entrepreneurial potential, problem-solving ability, managerial skills and achievement motivation, exercise in creativity, time audit, preparation of business plan and proposal writing, visit to entrepreneurship development institute and entrepreneurs
Geoinformatics and Nano-technology for Precision Farming
Theory
Precision agriculture: concepts and techniques; their issues and concerns for Indian agriculture; Geo-informatics- definition, concepts, tools and techniques; their use in Precision Agriculture. Crop discrimination and Yield monitoring, soil mapping; fertilizer recommendation using geospatial technologies; Spatial data and their management in GIS; Geodesy and its basic principles; Remote sensing concepts and application in agriculture; Image processing and interpretation; Global positioning system (GPS), components and its functions; System Simulation- Concepts and principles, Introduction to crop Simulation Models and their uses for optimization of Agricultural Inputs; STCR approach for precision agriculture; Nanotechnology, definition, concepts and techniques, brief introduction about nanoscale effects, nano-particles, nano-pesticides, nano-fertilizers, nano-sensors, Use of nanotechnology in tillage, seed, water, fertilizer, plant protection for scaling-up farm productivity.
Practical
Introduction to GIS software, spatial data creation and editing. Introduction to image processing software. Visual and digital interpretation of remote sensing images. Generation of spectral profiles of different objects. Supervised and unsupervised classification and acreage estimation. Multispectral remote sensing for soil mapping. Creation of thematic layers of soil fertility based on GIS. Creation of productivity and management zones. Fertilizer recommendations based on VRT and STCR techniques. Crop stress (biotic/abiotic) monitoring using geospatial technology. Use of GPS for agricultural survey. Formulation, characterization and applications of nanoparticles in agriculture. Project formulation and execution related to precision farming
Practical Crop Production-I (Kharif Crops)
Practical
Crop planning, raising field crops in multiple cropping systems: Field preparation, seed, treatment, nursery raising, sowing, nutrient, water and weed management and management of insect-pests diseases of crops, harvesting, threshing, drying winnowing, storage and marketing of produce. The emphasis will be given to seed production, mechanization, resource conservation and integrated nutrient, insect-pest and disease management technologies. Preparation of balance sheet including cost of cultivation, net returns per student as well as per team of 8-10 students.
Intellectual Property Rights
Theory
Introduction and meaning of intellectual property, a brief introduction to GATT, WTO, TRIPs and WIPO, Treaties for IPR protection: Madrid protocol, Berne Convention, Budapest treaty, etc.Types of Intellectual Property and legislations covering IPR in India:-Patents, Copyrights, Trademark, Industrial design, Geographical indications, Integrated circuits, and Trade secrets. Patents Act 1970 and Patent system in India, patentability, process and product patent, filing of patent, patent specification, patent claims, Patent opposition and revocation, infringement, Compulsory licensing, Patent Cooperation Treaty, Patent search and patent database. Origin and history including a brief introduction to UPOV for protection of plant varieties, Protection of plant varieties under UPOV and PPV&FR Act of India, Plant breeders rights, Registration of plant varieties under PPV&FR Act 2001, breeders, researcher and farmers rights. Traditional knowledge-meaning and rights of TK holders. Convention on Biological Diversity, International treaty on plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (ITPGRFA). Indian Biological Diversity Act, 2002 and its salient features, access and benefit sharing.
Other semesters syllabus and notes
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
related post-
What is bsc agriculture
BSc Agriculture means bachelor of science and birthplace of India...
Read More“Wheat Cultivation: Best Practices for High Yield & Profit (2025 Guide)”
Wheat cultivation is the backbone of global agriculture, feeding billions...
Read Moremahatma gandhi chitrakoot gramodaya vishwavidyalaya
Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramodaya University (MGCGV), formerly Gramodaya University and...
Read MoreIBPS Agriculture field officer: compleate guide to crack the exam
The IBPS Agriculture Field Officer (AFO) exam is a prestigious...
Read MoreAdvantages and Disadvantages of organic farming
Organic farming is the future of sustainable agriculture, offering chemical-free...
Read More






