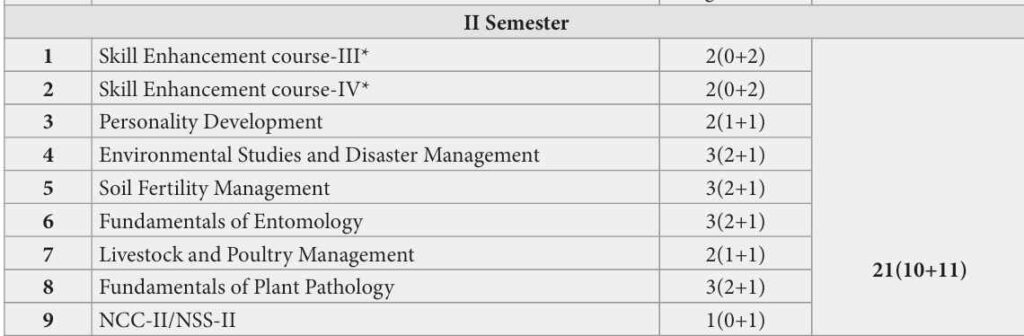
Download BSc agriculture 2nd semester syllabus and notes
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in Hindi.
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | Hindi Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in English
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Fundamentals of Genetics Credit
Theory
Pre and Post Mendelian concepts of heredity, Mendelian principles of heredity, Cell
division – mitosis, meiosis, Probability and Chi-square. Dominance relationships, gene
interaction.Multiple alleles, pleiotropism and pseudo alleles, Sex determination and sex linkage,
sex limited and sex influenced traits, Blood group genetics, Linkage and its estimation, crossing
over mechanisms, chromosome mapping. Structural changes in the chromosome, Mutation,
classification, Methods of inducing mutation & CIB technique, mutagenic agents and induction
of mutation. Qualitative & Quantitative traits, Polygenes and continuous variations, multiple
factor hypothesis, Epistatic interactions with examples. Cytoplasmic inheritance. Genetic
disorders,. Nature, structure & replication of genetic material. Protein synthesis, Transcription
and translational mechanism of genetic material, Gene concept: Gene structure, function and
regulation, Lac and Trp operons.
Practical
Study of the microscope. Study of cell structure. Experiments on monohybrid, dihybrid,
trihybrid, test cross and back cross, Experiments on epistatic interactions including test cross and
back cross, Practice on mitotic and meiotic cell division, Experiments on probability and Chi-
square test. Determination of linkage and cross-over analysis (through two-point test cross and
three-point test cross data). Study on sex-linked inheritance in Drosophila. Study of models on
DNA and RNA structure.
Download important books-
BSc agriculture 2nd semester syllabus and important books
Part – I
History of Entomology in India. Factors for insect abundance. Major points related to
the dominance of Insecta in the Animal kingdom. Classification of phylum Arthropoda up to classes.
Relationship of class Insecta with other classes of Arthropoda. Morphology: Structure and
functions of insect cuticle and moulting. Body segmentation. Structure of Head, thorax and
abdomen. Structure and modifications of insect antennae, mouth parts, legs, Wing venation,
modifications and wing coupling apparatus. Structure of male and female genital organs.
Metamorphosis and diapause in insects. Types of larvae and pupae. Structure and functions of
digestive, circulatory, excretory, respiratory, nervous, secretary (Endocrine) and reproductive
systems, in insects. Types of reproduction in insects. Major sensory organs like simple and
compound eyes, and chemoreceptors.
Part-II
Insect Ecology: Introduction, Environment and its components. Effect of abiotic factors–
temperature, moisture, humidity, rainfall, light, atmospheric pressure and air currents. Effect of
biotic factors – food competition, natural and environmental resistance. Concepts of Balance of life in nature, biotic potential and environmental resistance and causes for outbreak of pests in
agro-ecosystem.
Part III
Pest surveillance and pest forecasting. Categories of pests. Host plant resistance, Cultural,
Mechanical, Physical. Legislative. Biological (parasites, predators & transgenic plant pathogens
such as bacteria, fungi and viruses) methods of control. Chemical control-importance, hazards
and limitations. Classification of insecticides, toxicity of insecticides and formulations of
insecticides. Recent methods of pest control, repellents, antifeedants, hormones, attractants,
gamma radiation and genetic control. Practices, scope and limitations of IPM. Insecticides Act
1968-Important provisions. Application techniques of spray fluids. Phytotoxicity of insecticides.
Symptoms of poisoning, first aid and antidotes. Beneficial insects: parasites and predators used
in pest control and their mass multiplication techniques. Important groups of microorganisms,
bacteria, viruses and fungi are used in pest control and their mass multiplication techniques.
Important species of pollinators, weed killers and scavengers, their importance.
Part – IV
Systematics: Taxonomy –importance, history and development and binomial
nomenclature. Definitions of Biotype, Sub-species, Species, Genus, Family and Order.
Classification of class Insecta up to Orders, basic groups of present-day insects with special
emphasis to orders and families of Agricultural importance like Orthoptera: Acrididae,
Tettigonidae, Gryllidae, Gryllotalpidae; Dictyoptera: Mantidae, Blattidae; Odonata; Isoptera:
Termitidae; Thysanoptera: Thripidae; Hemiptera: Pentatomidae, Coreidae, Cimicidae,
Pyrrhocoridae, Lygaeidae, Cicadellidae, Delphacidae, Aphididae, Coccidae, Lophophidae,
Aleurodidae, Pseudococcidae; Neuroptera: Chrysopidae; Lepidoptera: Pieridae, Papiloinidae,
Noctuidae, Sphingidae, Pyralidae, Gelechiidae, Arctiidae, Saturnidae, Bombycidae; Coleoptera:
Coccinellidae, Chrysomelidae, Cerambycidae, Curculionidae, Bruchidae, Scarabaeidae;
Hymenoptera: Tenthridinidae, Apidae. Trichogrammatidae, lchneumonidae, Braconidae,
Chalcididae; Diptera: Cecidomyiidae, Tachinidae, Agromyziidae, Culicidae,Muscidae,
Tephritidae.
Practical
Methods of collection and preservation of insects including immature stages; External
features of Grasshopper/Blister beetle; Types of insect antennae, mouthparts and legs; Wing
venation, types of wings and wing coupling apparatus. Types of insect larvae and pupae;
Dissection of the digestive system in insects (Grasshopper); Dissection of male and female
reproductive systems in insects (Grasshopper); Study of characters of orders Orthoptera,
Dictyoptera, Odonata, Isoptera, Thysanoptera, Hemiptera, Lepidoptera, Neuroptera, Coleoptera,
Hymenoptera, Diptera and their families are of agricultural importance.
Fundamentals of Agricultural Economics
Theory
Economics: Meaning, scope and subject matter, definitions, activities, approaches to
economic analysis; micro and macroeconomics, positive and normative analysis. Nature of
economic theory; rationality assumption, concept of equilibrium, economic laws as a generalization of human behaviour. Basic concepts: Goods and services, desire, want, demand,
utility, cost and price, wealth, capital, income and welfare. Agricultural economics: meaning,
definition, characteristics of agriculture, importance and its role in economic development.
Agricultural planning and development in the country. Demand: meaning, the law of demand,
demand schedule and demand curve, determinants, utility theory; law of diminishing marginal
utility, equi-marginal utility principle. Consumer’s equilibrium and derivation of the demand curve,
the concept of consumer surplus. Elasticity of demand: concept and measurement of price elasticity,
income elasticity and cross elasticity. Production: process, creation of utility, factors of
production, input-output relationship. Laws of returns: Law of variable proportions and law of
returns to scale. Cost: Cost concepts, short-run and long-run cost curves. Supply: Stock v/s
supply, law of supply, supply schedule, supply curve, determinants of supply, elasticity of
supply. Market structure: meaning and types of market, basic features of perfectly competitive
and imperfect markets. Price determination under perfect competition; short run and long-run
equilibrium of firm and industry, shut down and break-even points. Distribution theory: meaning,
factor market and pricing of factors of production. Concepts of rent, wage, interest and profit.
National income: Meaning and importance, circular flow, concepts of national income
accounting and approaches to measurement, difficulties in measurement. Population:
Importance, Malthusian and Optimum population theories, natural and socioeconomic
determinants, current policies and programmes on population control. Money: Barter system of
exchange and its problems, evolution, meaning and functions of money, classification of money,
money supply, general price index, inflation and deflation. Banking: Role in a modern economy,
types of banks, functions of commercial and central bank, credit creation policy. Agricultural and
public finance: meaning, micro v/s macro finance, need for agricultural finance, public revenue
and public expenditure. Tax: meaning, direct and indirect taxes, agricultural taxation, VAT.
Economic systems: Concepts of the economy and its functions, important features of capitalistic,
socialistic and mixed economies, elements of economic planning.
BSc agriculture 2nd semester syllabus notes and important books
Fundamentals of Plant Pathology
Introduction: Importance of plant diseases, scope and objectives of Plant Pathology. History
of Plant Pathology with special reference to Indian work. Terms and concepts in Plant Pathology.
Pathogenesis.Cause and classification of plant diseases. Important plant pathogenic organisms,
different groups: fungi, bacteria, fastidious vesicular bacteria, phytoplasmas, spiroplasmas,
viruses, viroids, algae, protozoa, phanerogamic parasites and nematodes with examples of
diseases caused by them. Diseases and symptoms due to abiotic causes. Fungi: general
characters, definition of fungus, somatic structures, types of fungal thalli, fungal tissues,
modifications of thallus, reproduction (asexual and sexual). Nomenclature, Binomial system of
nomenclature, rules of nomenclature, classification of fungi. Key to divisions,sub-divisions,
orders and classes. Bacteria and mollicutes: general morphological characters. Basic methods of
classification and reproduction. Viruses: nature, architecture, multiplication and
transmission.Study of phanerogamic plant parasites. Nematodes: General morphology and
reproduction, classification, symptoms and nature of damage caused by plant nematodes
(Heterodera, Meloidogyne, Anguina etc.)Principles and methods of plant disease management.Nature, chemical combination, classification, mode of action and formulations of fungicides and
antibiotics.
Practical
Acquaintance with various laboratory types of equipment and microscopy. Preparation of media,
isolation and Koch’s postulates. General study of different structures of fungi. Study of symptoms
of various plant diseases. Study of representative fungal genera. Staining and identification of
plant pathogenic bacteria. Transmission of plant viruses. Study of phanerogamic plant parasites.
Study of morphological features and identification of plant parasitic nematodes. Extraction of
nematodes from soil. Study of fungicides and their formulations. Methods of pesticide
application and their safe use. Calculation of fungicide spray concentrations
Agricultural Extension Education
Theory
Education: Meaning, definition & Types; Extension Education- meaning, definition,
scope and process; objectives and principles of Extension Education; Extension Programme
planning- Meaning, Process, Principles and Steps in Programme Development. Extension
systems in India: extension efforts in pre-independence era (Sriniketan, Marthandam, Firka
Development Scheme, Gurgaon Experiment, etc.) and post-independence era (Etawah Pilot
Project, Nilokheri Experiment, etc.); various extension/ agriculture development programmes
launched by ICAR/ Govt. of India (IADP, IAAP, HYVP, KVK, IVLP, ORP, ND, NATP, NAIP,
etc.). New trends in agriculture extension: privatization extension, cyber extension/ e-extension,
market-led extension, farmer-led extension, expert systems, etc.Rural Development: concept,
meaning, definition; various rural development programmes launched by Govt. of India.
Community Dev.-meaning, definition, concept & principles, Physiology of C.D. Rural
Leadership: concept and definition, types of leaders in rural context; extension administration:
meaning and concept, principles and functions. Monitoring and evaluation: concept and
definition, monitoring and evaluation of extension programmes; transfer of technology: concept
and models, capacity building of extension personnel; extension teaching methods: meaning,
classification, individual, group and mass contact methods, media mix strategies;
communication: meaning and definition; models and barriers to communication. Agriculture
journalism; diffusion and adoption of innovation: concept and meaning, process and stages of
adoption, adopter categories.
Practical
To get acquainted with the university extension system. Group discussion- exercise; handling
and use of audio-visual equipment and digital camera and LCD projector; preparation and use of
AV aids, preparation of extension literature – leaflet, booklet, folder, pamphlet news stories and
success stories; Presentation skills exercise; micro-teaching exercise; A visit to village to
understand the problems being encountered by the villagers/ farmers; to study organization and
functioning of DRDA and other development departments at the district level; visits to NGOs and learning from their experience in rural development; understanding PRA techniques and their
application in village development planning; exposure to mass media: visit to community radio
and television studio for understanding the process of programme production; script writing,
writing for print and electronic media, and developing scripts for radio and television.
Communication Skills and Personality Development
Theory
Communication Skills: Structural and functional grammar; meaning and process of
communication, verbal and nonverbal communication; listening and note taking, writing skills,
oral presentation skills; field diary and lab record; indexing, footnote and bibliographic
procedures. Reading and comprehension of general and technical articles, precise writing,
summarizing, abstracting; individual and group presentations, impromptu presentation, public
speaking; and Group discussion. Organizing seminars and conferences.
Practical
Listening and note taking, writing skills, oral presentation skills; field diary and lab
record; indexing, footnote and bibliographic procedures. Reading and comprehension of general
and technical articles, precise writing, summarizing, abstracting; individual and group
presentations.
Fundamentals of Crop Physiology
Theory
Introduction to crop physiology and its importance in Agriculture; Plant cell: an
Overview; Diffusion and osmosis; Absorption of water, transpiration and Stomatal Physiology;
Mineral nutrition of Plants: Functions and deficiency symptoms of nutrients, nutrient uptake
mechanisms; Photosynthesis: Light and Dark reactions, C3, C4 and CAM plants; Respiration:
Glycolysis, TCA cycle and electron transport chain; Fat Metabolism: Fatty acid synthesis and
Breakdown; Plant growth regulators: Physiological roles and agricultural uses, Physiological
aspects of growth and development of major crops: Growth analysis, Role of Physiological
growth parameters in crop productivity.
Practical
Study of plant cells, structure and distribution of stomata, imbibitions, osmosis,
plasmolysis, measurement of root pressure, rate of transpiration, Separation of photosynthetic
pigments through paper chromatography, Rate of transpiration, photosynthesis, respiration,
tissue test for mineral nutrients, estimation of relative water content, Measurement of
photosynthetic CO2 assimilation by Infra-Red Gas Analyser (IRGA)
Agricultural Microbiology
Theory
Introduction. Microbial world: Prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes. Bacteria: cell
structure, chemoautotrophy, photo autotrophy, growth. Bacterial genetics: Genetic
recombination- transformation, conjugation and transduction, plasmids, transposon.
Role of microbes in soil fertility and crop production: Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and sulphur
cycles. Biological nitrogen fixation- symbiotic, associative and symbiotic. Azolla, blue-green
algae and mycorrhiza. Rhizosphere and phyllosphere. Microbes in human welfare: silage
production, biofertilizers, biopesticides, biofuel production and biodegradation.
Practical
Introduction to microbiology laboratory and its equipment; Microscope- parts, principles
of microscopy, resolving power and numerical aperture. Methods of sterilization. Nutritional
media and their preparations. Enumeration of microbial population in soil- bacteria, fungi,
actinomycetes. Methods of isolation and purification of microbial cultures. Isolation of
Rhizobium from legume root nodule. Isolation of Azotobacter from soil. Isolation of Azospirillum
from roots. Staining and microscopic examination of microbes.
Introductory Soil and Water Conservation Engineering
Theory
Introduction to Soil and Water Conservation, causes of soil erosion. Definition and agents
of soil erosion, water erosion: Forms of water erosion. Gully classification and control measures.
Soil loss estimation by universal Loss Soil Equation. Soil loss measurement techniques.
Principles of erosion control: Introduction to contouring, strip cropping. Contour bund. Graded
bund and bench terracing. Grassed waterways and their design. Water harvesting and its
techniques. Wind erosion: mechanics of wind erosion, types of soil movement. Principles of
wind erosion control and its control measures.
Practical
General status of soil conservation in India. Calculation of erosion index. Estimation of
soil loss. Measurement of soil loss. Preparation of contour maps. Design of grassed waterways.
Design of contour bunds. Design of graded bunds. Design of bench terracing system. Problem with
wind erosion.
Download important books-
BSc agriculture 2nd semester syllabus and important books
Other semester syllabus and notes
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Related post
What is bsc agriculture
BSc Agriculture means bachelor of science and birthplace of India...
Read More“Wheat Cultivation: Best Practices for High Yield & Profit (2025 Guide)”
Wheat cultivation is the backbone of global agriculture, feeding billions...
Read Moremahatma gandhi chitrakoot gramodaya vishwavidyalaya
Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramodaya University (MGCGV), formerly Gramodaya University and...
Read MoreIBPS Agriculture field officer: compleate guide to crack the exam
The IBPS Agriculture Field Officer (AFO) exam is a prestigious...
Read MoreAdvantages and Disadvantages of organic farming
Organic farming is the future of sustainable agriculture, offering chemical-free...
Read MoreRevolutionizing Indian Farming: The Role of Precision Agriculture in India
Precision agriculture in india “A friend of mine, Suresh Yadav,...
Read More







