
Basics of Agronomy History and its Scope PPT - First semester (part -1)
Fundamentals of Agronomy is an important subject for students of the BSc Agriculture in the first semester. In the first part of this subject, we begin with an introduction to agronomy, exploring its meaning, scope, and significance. This chapter will tell you what the role of agronomy is in modern agriculture, how it is connected to other agricultural sciences, and why this subject is like a foundation for every agriculture student.
In this part, you will get image-by-image visual PPT slides that explain the topic logically. Every slide has been carefully designed so that you can easily understand and get the concept clear, whether you are a BSc student or preparing for any exam.
👇 You will get the complete explanation of this topic in the images given below—step-by-step, visual, and exam-oriented format:
Topics covered:
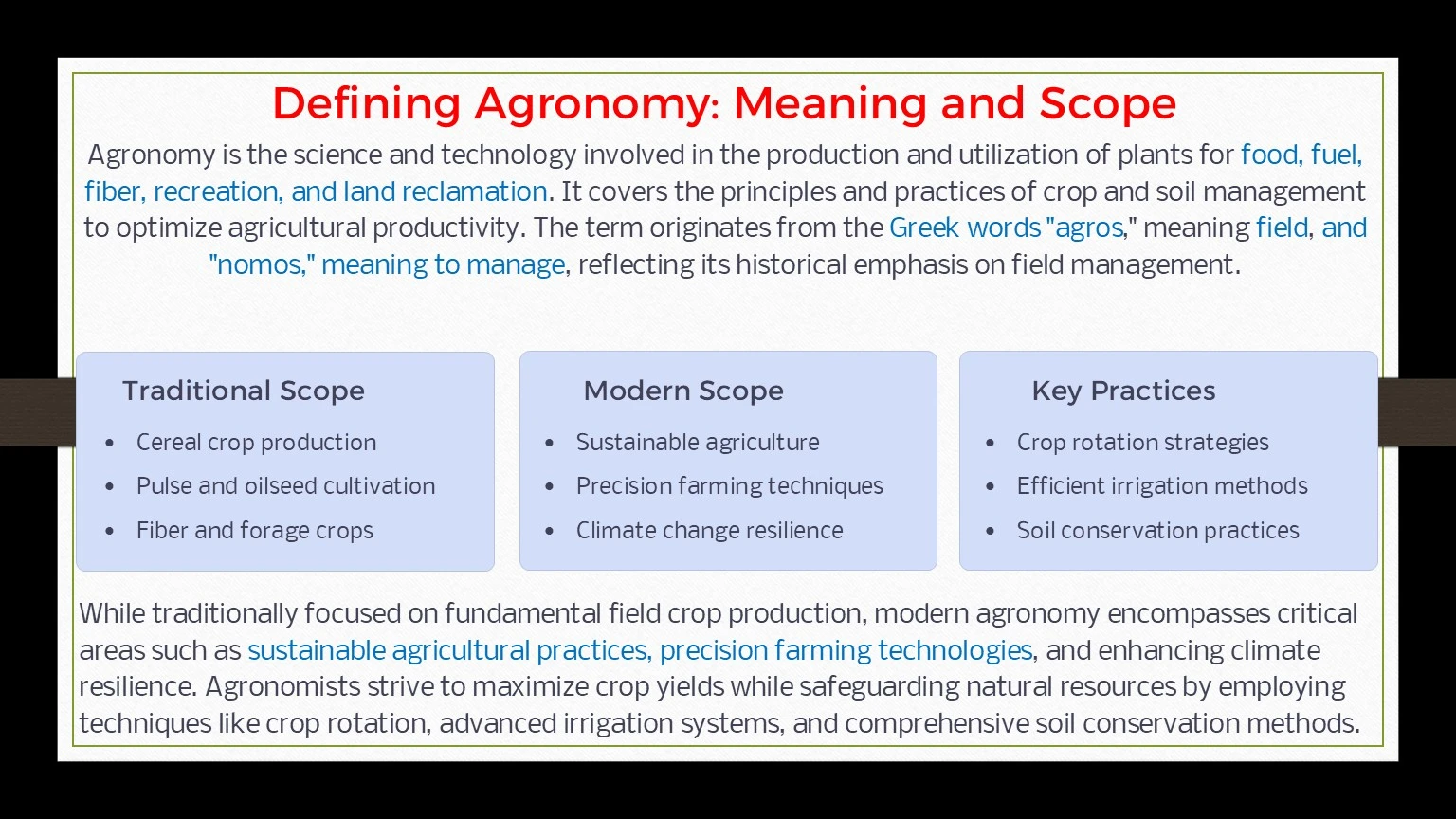
Definition, Meaning and Scope of Agronomy
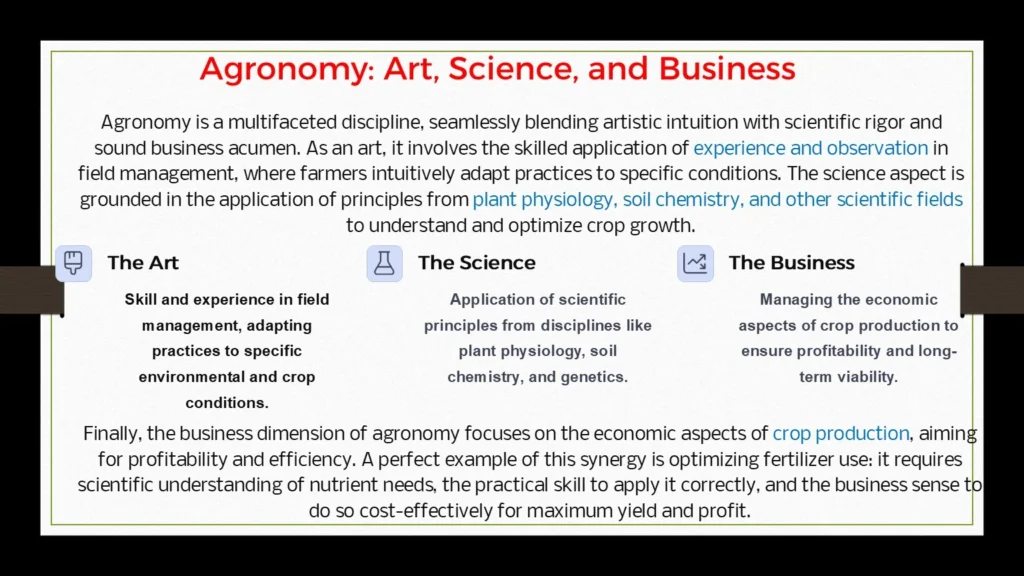
Agronomy as Art, Science, and Business of Crop Production
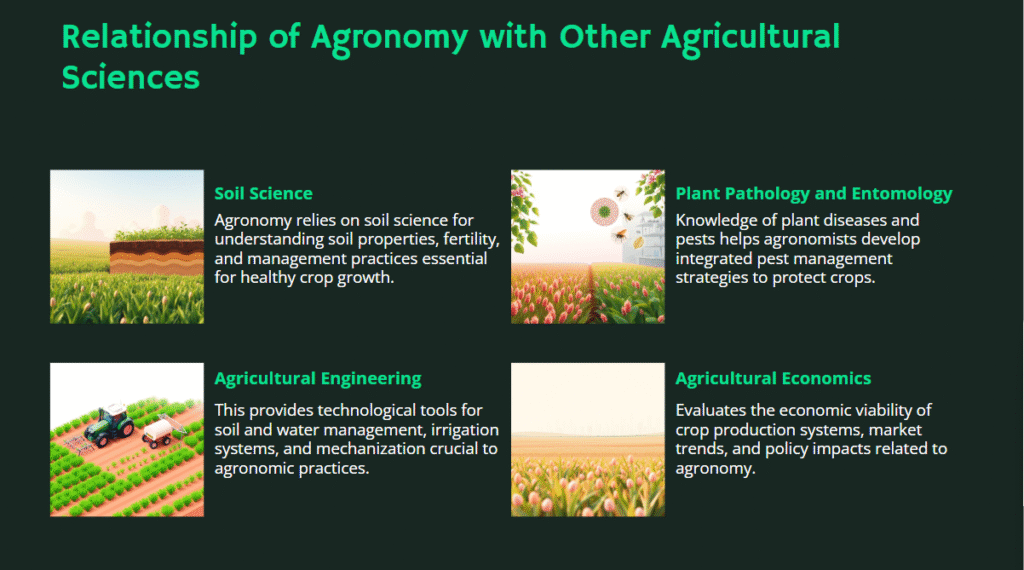
Relationship of Agronomy with Other Agricultural Sciences
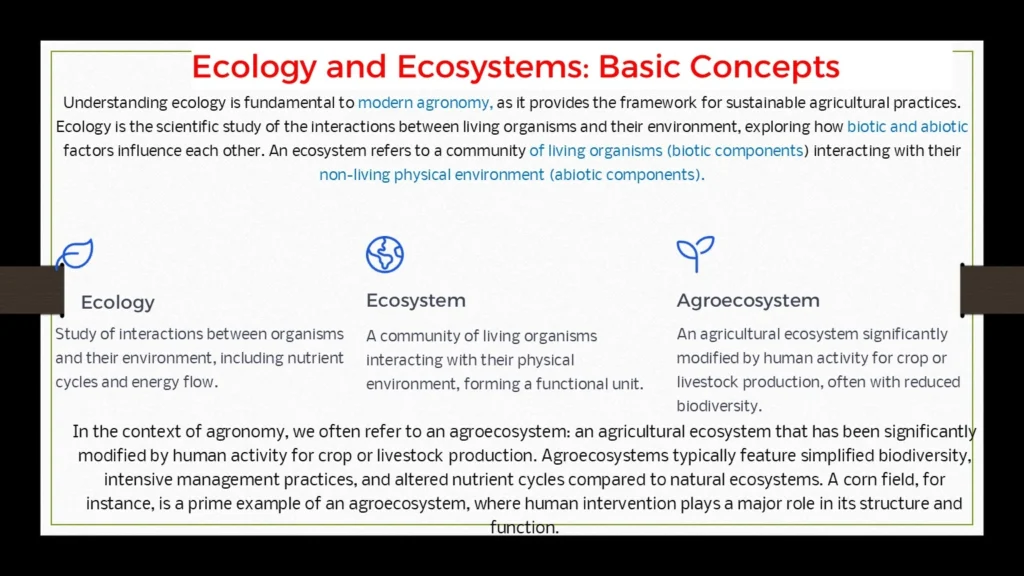
Ecology and Ecosystem—Basic Concepts in the Context of Agronomy
What is agriculture

What is agronomy


Defination of agronomy

Scopes of agronomy

History of agronomy

Agronomy's relation with other science

Future of agronomy?

10 PYQs from Basics of Agronomy History and its Scope (Part 1)—Asked in ICAR, AFO, etc.
1. Who among the following is known as the “Father of Agronomy”? (CG RAEO 2024)
A. D. N. Walia
B. Gregor Johann Mendel
C. Peter De Crescenzi
D. Stephen Hales
📝 Additional Information
Peter De Crescenzi (1230–1307 AD) compiled a treatise called Opus Ruralium Commentarum, considered the first systematic work on “agronomy” (the science of crop and soil management). That’s why he’s universally titled the “Father of Agronomy.”
D. N. Walia was a pioneer in Indian agro‐meteorology, not agronomy.
Gregor Johann Mendel is the “Father of Genetics,” known for pea‐plant inheritance experiments.
Stephen Hales is called the “Father of Plant Physiology” for his studies on root pressure and transpiration.
2. The size of a marginal landholding india is (UKPSC Prelims 2016)
A. More than 5 ha
B. 2 ha to 4 ha
C. 1 ha to 2 ha
D. Less than 1 ha
📝 Additional Information
Marginal holdings refer to land parcels held by very small farmers.
According to India’s Agriculture Census (2015–16), “marginal” is defined as < 1 ha.
Option A (More than 5 ha) would be a “large holding,” not marginal.
Option B (2 ha to 4 ha) and Option C (1 ha to 2 ha) are “semi‐medium” (2–4 ha) or “small” (1–2 ha) holdings, respectively.
3. The scope of Agronomy is the solution of: (CSJMU B.Sc Agriculture 1st Sem 2022)
A. Foodgrains
B. Fodder
C. Fibre
D. All of the above
📝 Additional Information
Agronomy deals with improving crop production and managing soils to suit various uses.
It covers Foodgrains (wheat, rice, maize), Fodder (gram, berseem, maize for livestock), and Fibre (cotton, jute, flax).
Therefore, saying “Foodgrains, Fodder, Fibre” all fall under agronomy’s domain is correct.
Option A, B, C alone would each be a subset, but the field manages all these, so All of the above is the only complete answer.
4. The “criteria of essentiality of mineral nutrients” for plants was coined by:(CSJMU B.Sc Agriculture 1st Sem 2022)
A. Liebig
B. Hoagland
C. Arnon & Stout
D. Watson
📝 Additional Information
In 1939, Arnon and Stout formulated three criteria to judge whether a mineral element is essential for plants:
Without that element, the plant cannot complete its life cycle.
No other element can replace it.
It is directly involved in plant metabolism.
Liebig laid the “Law of the Minimum” but did not formally phrase these “criteria.”
Hoagland developed the nutrient solution (Hoagland’s solution) for hydroponics, not the criteria.
Watson is known in plant genetics and molecular biology, not nutrient criteria.
5. Who among the following is referred to as the “Father of Agronomy”?(IBPS AFO Mains 2023)
A. Jethro Tull
B. Peter De Crescenzi
C. Louis Pasteur
D. M. S. Swaminathan
📝 Additional Information
In IBPS-AFO 2023, Peter De Crescenzi was the correct choice, for exactly the same reasons as in CG RAEO 2024.
Jethro Tull (1674–1741): pioneered the seed drill and is the “Father of Weed Science,” but not agronomy itself.
Louis Pasteur is the “Father of Microbiology,” not agronomy.
M. S. Swaminathan is often referred to as the “Father of the Green Revolution in India,” a notable distinction.
6. The term “agronomy” is derived from which language? (IBPS AFO Mains 2022)
A. Greek
B. Latin
C. American
D. Arabic
📝 Additional Information
Agronomy comes from two Greek words:
“Agros” = field
“Nomos” = to manage or law
Hence, it literally means “management of the field.”
Latin, American, or Arabic have no bearing here.
7. Which branch of agricultural science deals specifically with the art and science of crop production? (IBPS AFO Mains 2021)
A. Horticulture
B. Agronomy
C. Soil Science
D. Plant Pathology
📝 Additional Information
Agronomy is defined as the science of crop production and soil management.
Horticulture focuses on fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants, not broadfield crops.
Soil Science studies soil properties and fertility but does not include planting arrangement, sowing, etc., which agronomy does.
Plant Pathology is about plant diseases; it does not cover overall crop‐producing techniques.
8. The “criteria of essentiality of mineral nutrients” for higher plants was first proposed by:(ICAR JRF)
A. Liebig
B. Hoagland
C. Arnon & Stout
D. Watson
📝 Additional Information
This was very similar to CSJMU 2022. In ICAR‐JRF 2020, they asked the same principle: how to judge if an element is essential.
See the explanation in Q4 for why Arnon & Stout are correct.
Liebig, Hoagland, and Watson played important roles in plant nutrition or physiology but did not formulate those three “essentiality” points.
9. The scope of agronomy includes all except:(MPPEB RAEO 2019 )
A. Farm mechanization
B. Biotechnology
C. Crop production planning
D. Pesticide manufacturing
📝 Additional Information
Farm mechanization (implements, tractors, machinery for tillage) definitely comes under agronomy.
Biotechnology (e.g., developing crop varieties) is also integrated into modern agronomy, so they included that.
Pesticide manufacturing (the process of making herbicides, insecticides) is an agribusiness activity closely allied to agronomy, so it fit here.
Crop production planning—as they phrased it—was meant to be a broad administrative exercise rather than a hands‐on agronomic practice in that exam’s context. Hence, it was the “odd one out.”
10. Which of the following activities is part of agronomy? (NABARD Grade A Mains 2021)
A. Animal breeding
B. Extension education
C. Soil tillage
D. Plant pathology
📝 Additional Information
Soil tillage (plowing, harrowing, puddling) is a core agronomic operation used to prepare seedbeds, incorporate residues, and control weeds.
Animal breeding falls under animal husbandry, not agronomy.
Extension education is a separate field (Agri Extension).
Plant pathology deals with plant diseases.
Conclusion: Basics of Agronomy History and its Scope
Agronomy is the backbone of agriculture — it’s not just about the journey from seed to harvest but about understanding crops through a scientific, practical, and systematic lens.
Through this “Basics of Agronomy and Scopes PPT,” we’ve tried to simplify every concept so that it’s easy to understand, whether you’re a BSc Agriculture student or preparing for competitive agriculture exams. With visual notes, infographics, and MCQs, this resource is designed to make your study smart and effective.
👉 If you found this presentation helpful, let us know in the comments, and don’t forget to share it with your classmates and agri-friends.
👉 We’ll continue publishing visual notes for each syllabus part right here — so bookmark this website and keep checking for updates.
📩 Want a PPT on a specific topic or need exam guidance? Just let us know below — AgriGramodaya is your learning platform.
🎯 Click below to access the complete topic-wise content, MCQs, and presentations designed to help you master agronomy step by step:
👉 [Go to the Main Agronomy Page Now]
Click to Join Our Free WhatsApp Group for Agriculture Updates!
Get daily updates, free study material, and the latest schemes, and connect with other agriculture students and farmers.
Read more fundamentals of agronomy Topics
Important message
📥 Want This PPT for Personal Use?
If you want this full presentation in PPT format for offline study or classroom use, feel free to message me personally on WhatsApp.
I’ll be happy to share it with you!
📲 WhatsApp 9343512089
📝 Note: This is for educational purposes only. Please don’t redistribute without permission.
Agricultural students also ask
Agronomy is the science and practice of growing crops. It includes everything from soil preparation, sowing, irrigation, fertilizers, to harvesting — to increase both productivity and sustainability.
Agronomy helps farmers make better decisions about crops, soil, water, and fertilizers. It improves yield, saves resources, and promotes sustainable farming.
Agronomy has a wide scope in research, teaching, crop management, agri-business, competitive exams, and even startups in organic farming and precision agriculture.
Agriculture is a broad field that includes crop production, animal husbandry, forestry, etc. Agronomy is a branch of agriculture that specifically deals with crop science and soil management.
This post gives you visually-rich, easy-to-grasp content in image format — faster to revise, better for memory, and more engaging than long theory.
Yes! You can comment or contact us with your topic request, and we’ll try to provide visual notes or blog content for it soon.
After bsc agriculture exam (New Syllabus )
Latest Syllabus | Download Here |
IBPS Agriculture Filed Officer | |
NABARD GRADE A | |
Food Corporation of India (FCI) | |
RAEO | |
RHEO | |
Food Inspector | |
IFFCO AGT | |
MP PAT | |
UPSSSC AGTA |
Read B.Sc. agriculture syllabus and notes
Related post
👉Top 100 Crop Improvement in Rabi Crops MCQs + Fill in Blanks + One Liners (Exam Special)
Crop improvement in rabi crops MCQs is one of the...
Read More👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More🙋♂️ About the Author
Khumesh, a BSc Agriculture student and founder of AgriGramodaya.com, is on a mission to make “Fundamentals of Agronomy” the easiest and most accessible subject for students across India.
Having personally faced the challenge of finding clear, structured, and visual content for Agronomy, he decided to build a complete one-page resource, breaking down the full syllabus into simple parts — supported by PPTs, summary notes, previous-year MCQs, and exam-oriented insights.
Every part of this subject is designed to help students from zero to advanced level, whether you’re preparing for semester exams or agriculture job exams.
📚 Learn visually. Revise smartly. Succeed confidently — only on AgriGramodaya.


