BSc agriculture 1st semester notes in english and hindi
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in Hindi.
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | Hindi Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Download other 1st, 2nd , 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th semester notes PDF in English
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
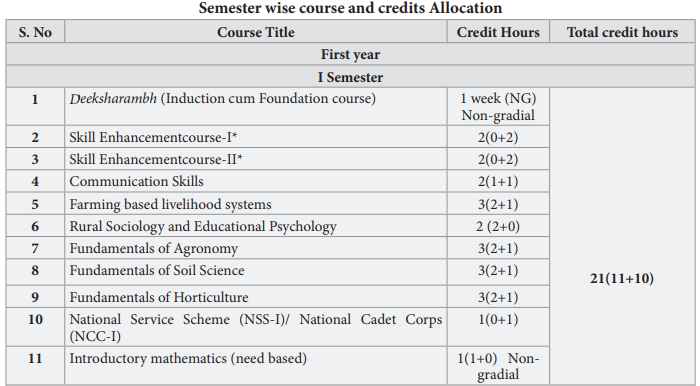
BSc Agriculture 1st semester notes and syllabus
Fundamentals of Horticulture
Theory
Horticulture-Its definition and branches, importance and scope; horticultural and
botanical classification; climate and soil for horticultural crops; Plant propagation-methods and
propagating structures; principles of orchard establishment; Principles and methods of training
and pruning, juvenility and flower bud differentiation; unfruitfulness; pollination, pollinizers and
pollinators; fertilization and parthenocarpy; kitchen gardening; garden types and parts; lawn
making; medicinal and aromatic plants; species and condiments; use of plant bio-regulators in
horticulture. Irrigation & fertilizers application and quantity.
Practical
Identification of garden tools. Identification of horticultural crops. Preparation of seed
bed/nursery bed. Practice of sexual and asexual methods of propagation. Layout and planting of
orchard plants. Training and pruning of fruit trees. Transplanting and care of vegetable seedlings.
Making of herbaceous and shrubbery borders. Preparation of potting mixture, potting an
Theory
Agronomy and its scope, seeds and sowing, tillage and tilth, crop density and geometry,
Crop nutrition, manures and fertilizers, nutrient use efficiency, water resources, soil plant water
relationship, crop water requirement, water use efficiency, irrigation-scheduling criteria and
methods, quality of irrigation water, and water logging. Weeds- importance, classification, crop weed
competition, concepts of weed management-principles and methods, herbicides- classification,
selectivity and resistance, allelopathy. Growth and development of crops, factors affecting
growth and development, plant ideotypes, crop rotation and its principles, adaptation and
distribution of crops, crop management technologies in problematic areas, harvesting and
threshing of crops.
Practical
Identification of crops, seeds, fertilizers, pesticides and tillage implements, Effect of
sowing depth on germination and seedling vigour, Identification of weeds in crops, Methods of
herbicide and fertilizer application, Study of yield contributing characters and yield estimation,
Seed germination and viability test, Numerical exercises on fertilizer requirement, plant
population, herbicides and water requirement, Use of tillage implements-reversible plough, one
way plough, harrow, leveller, seed drill, Study of soil moisture measuring devices, Measurement
of field capacity, bulk density and infiltration rate, Measurement of irrigation water.
BSc agriculture 1st semester notes and important books
Fundamentals of Soil Science
Theory
Soil as a natural body, Pedological and edaphological concepts of soil; Soil genesis: soil
forming rocks and minerals; weathering, processes and factors of soil formation; Soil Profile,
components of soil; Soil physical properties: soil texture, structure, density and porosity, soil
colour, consistency and plasticity; Elementary knowledge of soil taxonomy classification and
soils of India; Soil water retention, movement and availability; soil air, composition, gaseous
exchange, problem and plant growth; source, amount and flow of heat in soil; soil temperature
and plant growth; Soil reaction-pH, soil acidity and alkalinity, buffering, effect of pH on nutrient
availability; soil colloids – inorganic and organic; silicate clays: constitution and properties;
sources of charge ion exchange, cation exchange capacity, base saturation; soil organic matter:
composition, properties and its influence on soil properties; humic substances – nature and
properties; soil organisms: macro and microorganisms, their beneficial and harmful effects; Soil
pollution – behaviour of pesticides and inorganic contaminants, prevention and mitigation of soil
pollution.
Practical
Study of soil profile in the field. Study of soil sampling tools, collection of representative soil
samples, its processing and storage. Study of soil forming rocks and minerals. Determination of
soil density, moisture content and porosity. Determination of soil texture by feel and Bouyoucos
Methods. Studies of capillary rise phenomenon of water in soil column and water movement in
soil. Determination of soil pH and electrical conductivity. Determination of cation exchange
capacity of soil. Study of soil map. Determination of soil colour. Demonstration of heat transfer
in soil. Estimation of the organic matter content of soil.
Rural Sociology & Educational Psychology
Theory
Sociology and Rural Sociology: Definition and Scope, its Significance in agriculture
extension, Rural society, Social Groups, Social Stratification, Culture concept, Social Institution,
Social Change & Development. Educational psychology: Meaning & its importance in
agriculture extension. Behaviour: Cognitive, affective, psychomotor domain, Personality,
Learning, Motivation, Theories of Motivation, Intelligence.
Fundamentals of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology
Theory
Importance of Biochemistry. Properties of Water, pH and Buffer. Carbohydrate:
Importance and classification. Structures of Monosaccharides, Reducing and oxidizing
properties of Monosaccharides, Mutarotation; Structure of Disaccharides and Polysaccharides.Lipid: Importance and classification; Structures and properties of fatty acids; storage lipids and
membrane lipids. Proteins: Importance of proteins and classification; Structures, titration and
zwitterions nature of amino acids; Structural organization of proteins. Enzymes: General
properties; Classification; Mechanism of action; Michaelis & Menten and Line Weaver Burk
equation & plots; Introduction to allosteric enzymes. Nucleic acids: Importance and
classification; Structure of Nucleotides, A, B & Z DNA; RNA: Types and Secondary & Tertiary
structure. Metabolism of carbohydrates: Glycolysis, TCA cycle, Glyoxylate cycle, Electron
transport chain. Metabolism of lipids: Beta oxidation, Biosynthesis of fatty acids. Concepts and
applications of plant biotechnology: Scope, organ culture, embryo culture, cell suspension
culture, callus culture, anther culture, pollen culture and ovule culture and their applications;
Micro-propagation methods; organogenesis and embryogenesis, Synthetic seeds and their
significance; Embryo rescue and its significance; somatic hybridization and cybrids;
Somaclonal variation and its use in crop improvement; cryo-preservation; Introduction to
recombinant DNA methods: physical (Gene gun method), chemical (PEG mediated) and
Agrobacterium mediated gene transfer methods; Transgenics and its importance in crop
improvement; PCR techniques and its applications; RFLP, RAPD, SSR; Marker Assisted
Breeding in crop improvement; Biotechnology regulations.
Practical
Preparation of solution, pH & buffers, Qualitative tests of carbohydrates and amino acids.
Quantitative estimation of glucose/ proteins. Titration methods for estimation of amino
acids/lipids, Effect of pH, temperature and substrate concentration on enzyme action, Paper
chromatography/ TLC demonstration for separation of amino acids/ Monosaccharides.
Sterilization techniques. Composition of various tissue culture media and preparation of stock
solutions for MS nutrient medium. Callus induction from various explants. Micro-propagation,
hardening and acclimatization. Demonstration on isolation of DNA. Demonstration of gel
electrophoresis techniques and DNA fingerprinting.
Introduction to Forestry
Theory
Introduction – definitions of basic terms related to forestry, objectives of silviculture,
forest classification, and salient features of Indian Forest Policies. Forest regeneration, Natural
regeneration – natural regeneration from seed and vegetative parts, coppicing, pollarding, root
suckers; Artificial regeneration – objectives, the choice between natural and artificial regeneration,
essential preliminary considerations. Crown classification. Tending operations – weeding,
cleaning, thinning – mechanical, ordinary, crown and advanced thinning. Forest mensuration –
objectives, diameter measurement, instruments used in diameter measurement; Non-instrumental
methods of height measurement – shadow and single pole method; Instrumental methods of
height measurement – geometric and trigonometric principles, instruments used in height
measurement; tree stem form, form factor, form quotient, measurement of the volume of felled and
standing trees, age determination of trees. Agroforestry – definitions, importance, criteria of
selection of trees in agroforestry, different agroforestry systems prevalent in the country, shifting
cultivation, tangy, alley cropping, windbreaks and shelter belts, home gardens. Cultivation
practices of two important fast-growing tree species of the region.
Practical
Identification of tree species. Diameter measurements using callipers and tape, diameter
measurements of forked, buttressed, fluted and leaning trees. Height measurement of standing
trees by shadow method, single pole method and hypsometer. Volume measurement of logs
using various formulae. Nursery layout, seed sowing, vegetative propagation techniques. Forest
plantations and their management. Visits of nearby forest-based industries.
Comprehension and Communication Skills in English
Theory
War minus Shooting- The Sporting Spirit. A Dilemma- A layman looks at science
Raymond B. Fosdick. You and Your English – Spoken English and broken English G.B. Shaw.
Reading Comprehension, Vocabulary- Antonym, Synonym, Homophones, Homonyms, often
confused words. Exercises to Help the students in the enrichment of vocabulary based on
TOEFL and other competitive examinations. Functional grammar: Articles, Prepositions, Verb,
Subject-verb Agreement, Transformation, Synthesis, Direct and Indirect Narration. Written
Skills: Paragraph writing, Precise writing, Report writing and Proposal writing. The Style:
Importance of professional writing. Preparation of Curriculum Vitae and Job applications.
Synopsis Writing. Interviews: kinds, Importance and process.
Practical
Listening Comprehension: Listening to short talks lectures, speeches (scientific,
commercial and general in nature). Oral Communication: Phonetics, stress and intonation,
Conversation practice. Conversation: rate of speech, clarity of voice, speaking and Listening,
politeness & Reading skills: reading dialogues, rapid reading, intensive reading, improving
reading skills. Mock Interviews: testing initiative, team spirit, leadership, intellectual ability.
Group Discussions.
Human Value and Ethics
Theory
Values and Ethics-An Introduction. Goal and Mission of Life. Vision of Life. Principles
and Philosophy. Self Exploration. Self Awareness. Self Satisfaction. Decision Making.
Motivation. Sensitivity. Success. Selfless Service. Case Study of Ethical Lives. Positive Spirit.
Body, Mind and Soul. Attachment and Detachment. Spirituality Quotient. Examination.
Agriculture Heritage
Theory
Introduction of Indian agricultural heritage, the status of farmers in society; advice by sages
to kings on their duties towards farmers, soil management in ancient, medieval & pre-modern
India and its relevance in modern-day sustainable agriculture, the heritage of crop & water
management, plant growth and development & plant protection through Vrikshayurveda and
traditional knowledge. Heritage of medicinal plants and their relevance today, seed health in
ancient & medieval history and its relevance to present-day agriculture, description of Indian
civilization and agriculture by travellers from China, Europe and the United States, our journey in
agriculture, green revolution and its impact and concerns, and vision for the future.
Introductory Biology
Theory
Introduction to the living world, diversity and characteristics of life, origin of life,
Evolution and Eugenics. Binomial nomenclature and classification Cell and cell division.
Morphology of flowering plants. Seed and seed germination. Plant systematic- viz; Brassicaceae,
Fabaceae and Poaceae. Role of animals in agriculture.
Practical
Morphology of flowering plants – root, stem and leaf and their modifications. Inflorence,
flowers and fruits. Cell, tissues & cell division. Internal structure of root, stem and leaf. Study of
specimens and slides. Description of plants – Brassicaceae, Fabaceae and Poaceae.
Elementary Mathematics
Theory
Straight lines: Distance formula, section formula (internal and external division), Change
of axes (only origin changed), Equation of co-ordinate axes, Equation of lines parallel to axes,
The slope-intercept form of the equation of a line, Slope-point form of the equation of the line, Two point form of
equation of the line, Intercept form of the equation of the line, Normal form of equation of a line, General
form of equation of the line, Point of intersection of two st. lines, Angles between two st. lines,
Parallel lines, Perpendicular lines, Angle of bisectors between two lines, the Area of the triangle and
quadrilateral. Circle: Equation of circle whose centre and radius are known, General equation of a
circle, Equation of a circle passing through three given points, Equation of a circle whose diameters
is a line joining two points (x1, y1) & (x2,y2), Tangent and Normal to a given circle at a given point
(Simple problems), Condition of tangency of a line y = mx + c to the given circle x2
+ y2
=
a
2
.Differential Calculus: Definition of function, limit and continuity, Simple problems on limit,
Simple problems on continuity, Differentiation of xn
, ex
, sin x & cos x from first principle,
Derivatives of sum, difference, product and quotient of two functions, Differentiation of
functions of functions (Simple problem based on it), Logarithmic differentiation (Simple
problem-based on it), Differentiation by substitution method and simple problems based on it, and Differentiation of Inverse Trigonometric functions. Maxima and Minima of the functions of the
form y=f (x) (Simple problems based on it).
Integral Calculus: Integration of simple functions, Integration of Product of two functions,
Integration by substitution method, Definite Integral (simple problems based on it), Area under
simple well-known curves (simple problems based on it).
Matrices and Determinants: Definition of Matrices, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication,
Transpose and Inverse up to 3rd order, Properties of determinants up to 3rd order and their
evaluation.
Other bsc agriculture semester notes and syllabus click and downloads
BSc agriculture 1st semester notes and important books
BSc Ag. Semseter Name | English Notes PDFs |
1st semester | |
2nd semester | |
3rd semester | |
4th semester | |
5th semester | |
6th semester |
Related post-
What is bsc agriculture
BSc Agriculture means bachelor of science and birthplace of India...
Read More“Wheat Cultivation: Best Practices for High Yield & Profit (2025 Guide)”
Wheat cultivation is the backbone of global agriculture, feeding billions...
Read Moremahatma gandhi chitrakoot gramodaya vishwavidyalaya
Mahatma Gandhi Chitrakoot Gramodaya University (MGCGV), formerly Gramodaya University and...
Read MoreIBPS Agriculture field officer: compleate guide to crack the exam
The IBPS Agriculture Field Officer (AFO) exam is a prestigious...
Read More





