Physical Properties Of Soil MCQ 2025
Soil is the foundation of agriculture, and its physical properties play a crucial role in plant growth, water retention, and nutrient availability. Understanding soil texture, structure, porosity, bulk density, and water-holding capacity is essential for effective soil management and crop productivity.
In this MCQ series, we present 10+ multiple-choice questions (MCQs) on the physical properties of soil with detailed explanations. These questions are highly relevant for competitive exams like IBPS AFO, NABARD, FCI, ICAR-JRF, and state agriculture exams. Whether you are a BSc Agriculture student, farmer, or soil science enthusiast, these MCQs will strengthen your understanding of important soil concepts.
Let’s test your knowledge and enhance your preparation!

Physical Properties Of Soil MCQ PDF Download
1. Which soil property determines its ability to retain and drain water?
A) Soil texture
B) Soil color
C) Soil temperature
D) Soil fertility
📝 Additional Information
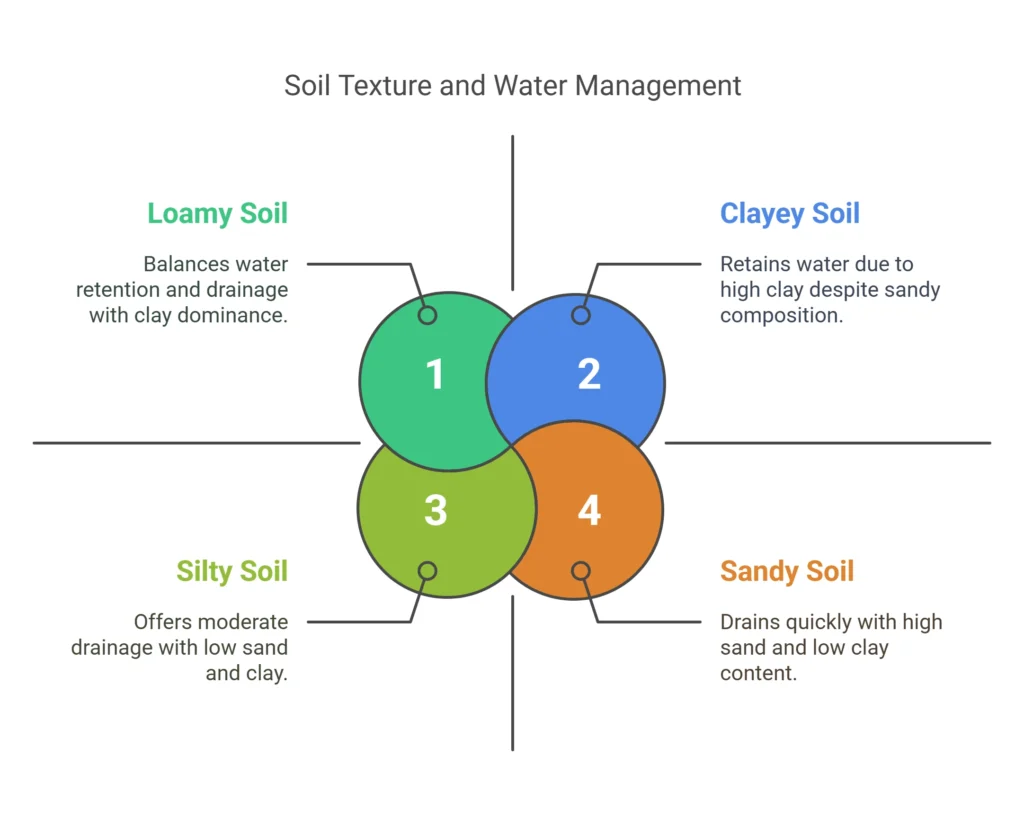
Soil texture refers to the relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay in the soil, which influences its water-holding capacity and drainage.
Sandy soils drain water quickly but hold less moisture, while clayey soils retain water for a longer duration.
Loamy soil (a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay) has optimal water retention and drainage properties.
Soil color, temperature, and fertility do not directly determine water movement in the soil.
2. What is the bulk density of an ideal agricultural soil?
A) 0.5 – 0.9 g/cm³
B) 1.0 – 1.6 g/cm³
C) 2.0 – 2.5 g/cm³
D) 3.0 – 3.5 g/cm³
📝 Additional Information
Bulk density is the mass of soil per unit volume and affects root penetration and water movement.
Loose, well-aerated soils have a lower bulk density (1.0 – 1.3 g/cm³), which is good for root growth.
Compacted soils (above 1.6 g/cm³) restrict root penetration and reduce aeration.
Higher bulk density is common in subsurface layers or overgrazed lands, making them less suitable for farming.
3. What is the main function of soil porosity?
A) To store and transport air and water
B) To determine soil color
C) To increase soil temperature
D) To convert sand into clay
📝 Additional Information
Soil porosity refers to the percentage of pore space in the soil. It determines air circulation, water retention, and drainage.
Sandy soils have large pores (macropores) that allow quick drainage but low water retention.
Clayey soils have small pores (micropores), which retain water but slow down aeration.
Soil color, temperature, or sand-clay conversion are unrelated to porosity.
4. What determines the color of soil?
A) Organic matter and mineral composition
B) Soil porosity
C) pH of soil
D) Bulk density
📝 Additional Information
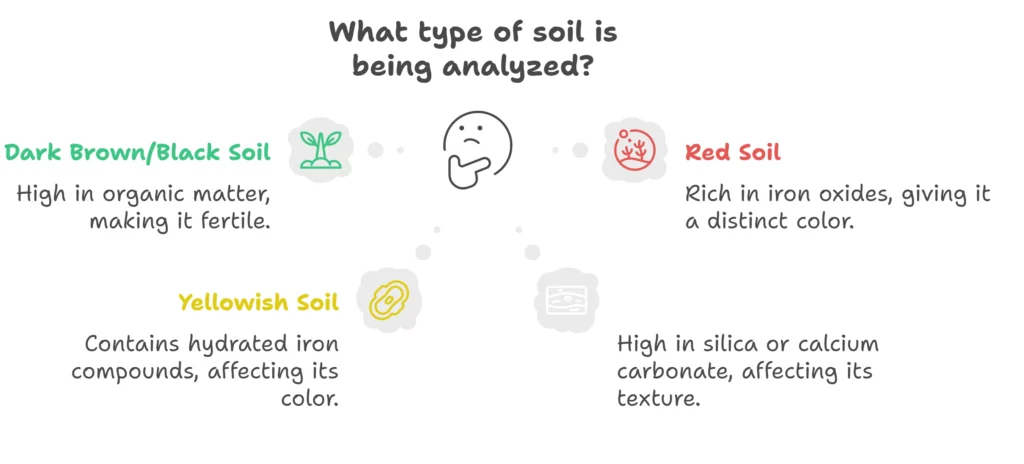
Dark brown or black soil contains high organic matter (humus), making it fertile.
Red soil is rich in iron oxides (Fe₂O₃).
Yellowish soil contains hydrated iron compounds.
Whitish soil may have high silica or calcium carbonate content.
5. Which soil type has the highest water-holding capacity?
A) Sandy soil
B) Clayey soil
C) Loamy soil
D) Gravelly soil
📝 Additional Information
Clayey soil has fine particles and high porosity, allowing it to retain large amounts of water.
Sandy soil drains quickly, making it less suitable for water retention.
Loamy soil holds moderate water, making it best for agriculture.
Gravelly soil has poor water retention.
Related soil science MCQ
5. The Dust Bowl (1930s) was primarily caused by:
A) Overgrazing + drought
B) Excessive irrigation
C) Volcano eruptions
D) Deforestation
6. How does soil structure affect plant growth?
A) Improves root penetration and nutrient absorption
B) Increases soil acidity
C) Reduces microbial activity
D) Enhances soil color
📝 Additional Information
Good soil structure allows better aeration, water movement, and root growth.
Granular or crumb-like structures are ideal for agriculture.
Compacted soils restrict root development and limit nutrient uptake.
7. What is the term for the ability of soil to resist deformation and retain its shape?
A) Soil strength
B) Soil plasticity
C) Soil texture
D) Soil porosity
📝 Additional Information
Soil strength determines how well soil resists stress and supports structures (roots, buildings).
Loose sandy soils have low strength, while clayey soils have higher strength.
Soil plasticity refers to its ability to be molded when wet.
8. What is the ideal soil temperature for seed germination?
A) 5-10°C
B) 15-30°C
C) 35-45°C
D) Above 50°C
📝 Additional Information
Soil temperature affects seed germination, root development, and microbial activity.
Most crops germinate well between 15-30°C.
Too low or too high temperatures reduce seedling survival.
9. What is the term for the movement of air through soil pores?
A) Soil aeration
B) Soil erosion
C) Soil compaction
D) Soil drainage
📝 Additional Information
Soil aeration allows oxygen to reach plant roots and soil microbes.
Poor aeration leads to root suffocation and reduced microbial activity.
Compacted soils have poor aeration.
10. What is the term for soil’s ability to retain nutrients?
A) Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
B) Soil porosity
C) Soil erosion
D) Soil texture
📝 Additional Information
CEC measures soil’s ability to hold and exchange nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Higher CEC means better nutrient retention.
Clayey and organic soils have high CEC.
11. Which soil property determines how easily air and water move through it?
A) Soil permeability
B) Soil texture
C) Soil color
D) Soil strength
📝 Additional Information
Soil permeability refers to how easily air and water can pass through soil pores.
Sandy soils have high permeability, meaning they drain quickly.
Clayey soils have low permeability, meaning they retain water longer.
Soil texture, color, and strength influence permeability but do not define it directly.
12. Which soil type is best for agriculture based on its physical properties?
A) Sandy soil
B) Clayey soil
C) Loamy soil
D) Gravelly soil
📝 Additional Information
Loamy soil has a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, making it ideal for agriculture.
It provides good aeration, drainage, and water retention—essential for healthy plant growth.
Sandy soil drains too quickly, while clayey soil holds too much water, making them less suitable for most crops.
13. Which factor does NOT directly affect soil temperature?
A) Soil color
B) Soil organic matter
C) Soil pH
D) Soil moisture
📝 Additional Information
Soil temperature is influenced by color (dark soils absorb more heat), moisture (wet soils heat up slowly), and organic matter (affects heat absorption and retention).
Soil pH affects nutrient availability but has no direct impact on soil temperature.
14. What is the term for the ability of soil to resist water penetration?
A) Infiltration rate
B) Soil permeability
C) Soil porosity
D) Water repellency
📝 Additional Information
Some soils, especially those with high organic matter or hydrophobic coatings, resist water absorption.
This leads to poor infiltration and increased runoff.
Farmers use mulching and organic amendments to reduce water repellency.
15. Which physical property of soil affects its ability to withstand pressure?
A) Soil structure
B) Bulk density
C) Soil color
D) Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
📝 Additional Information
Bulk density measures how compact the soil is—higher values indicate more compacted soil.
Compacted soils reduce root growth and water infiltration.
Loose soils (low bulk density) are better for plant growth.
16. What happens when soil has poor aeration?
A) Roots grow faster
B) Microbial activity increases
C) Oxygen levels decrease
D) Soil temperature rises
📝 Additional Information
Poor aeration means less oxygen is available for plant roots and soil microbes.
This leads to anaerobic conditions, which harm plant growth.
Waterlogged soils have very low oxygen levels, causing root rot.
17. What is the process of water movement within soil called?
A) Infiltration
B) Erosion
C) Compaction
D) Leaching
📝 Additional Information
Infiltration refers to the entry of water into the soil surface.
Permeability determines how fast it moves deeper.
Leaching occurs when water carries nutrients downward.
18. What does a high cation exchange capacity (CEC) in soil indicate?
A) High nutrient-holding capacity
B) Poor soil structure
C) High water drainage
D) Low fertility
📝 Additional Information
CEC measures soil’s ability to hold and exchange nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Clay and organic matter increase CEC, making soil more fertile.
19. Which physical property is most important for seed germination?
A) Soil color
B) Soil texture
C) Soil temperature
D) Soil pH
📝 Additional Information
Seeds require an optimal temperature (15-30°C) for germination.
Too high or too low temperatures delay or stop germination.
Upcoming agriculture exams 2025
20. Which soil property prevents water from moving downward?
A) Soil texture
B) Soil aeration
C) Compaction
D) Soil structure
📝 Additional Information
Compacted soils have fewer pores, reducing water movement.
Roots struggle to penetrate compacted soil.
21. What is the term for the movement of water through soil pores?
A) Infiltration
B) Percolation
C) Capillary action
D) Evaporation
📝 Additional Information
Percolation refers to the downward movement of water through soil pores after infiltration.
It affects groundwater recharge and soil moisture availability for deep-rooted crops.
Sandy soils have fast percolation rates, while clayey soils have slow percolation rates.
22. Which soil texture has the highest surface area and water-holding capacity?
A) Sandy soil
B) Loamy soil
C) Silty soil
D) Clayey soil
📝 Additional Information
Clay particles are the smallest in size but have the highest surface area, which allows them to hold more water.
This results in poor drainage and slow infiltration.
Sandy soils drain quickly, while loamy soils have a balanced water-holding capacity.
23. What is the primary cause of soil aggregation?
A) Organic matter and microorganisms
B) High sand content
C) Soil erosion
D) Excessive tillage
📝 Additional Information
Soil aggregation is the process where soil particles bind together to form stable clumps.
Organic matter (like humus) and soil microorganisms play a vital role in aggregation.
Excessive tillage can break soil aggregates, making the soil more prone to erosion.
24. Which soil property influences its ability to exchange nutrients with plant roots?
A) Bulk density
B) Soil texture
C) Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
D) Soil porosity
📝 Additional Information
CEC measures the soil’s ability to hold and release essential nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Clayey and organic matter-rich soils have high CEC, meaning they retain more nutrients.
Sandy soils have low CEC, leading to nutrient leaching.
25. Which factor most affects soil color?
A) Organic matter and mineral content
B) Soil moisture
C) pH level
D) Soil porosity
📝 Additional Information
Dark-colored soils indicate high organic matter, which improves fertility.
Red and yellow soils contain iron oxides, which are common in well-drained areas.
Gray and bluish soils suggest poor drainage and waterlogging due to iron reduction.
Related MCQs
👉Top 100 Crop Improvement in Rabi Crops MCQs + Fill in Blanks + One Liners (Exam Special)
Crop improvement in rabi crops MCQs is one of the...
Read More👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More80+ Post Harvest Management MCQs, Fill in the Blanks & Short Questions (Exam-Oriented)
Post harvest management is one of the most important units...
Read MoreR.S. Singh Plant Diseases Book PDF: The “Gift” for Plant Pathology Students
Table of Contents If you are a BSc Agriculture student,...
Read More



