Author- Khumesh Choudhary

6th Dean Committee Agriculture Syllabus
Have you ever wondered what the future of farming and agriculture will look like in a world driven by technology, sustainability, and innovation? Well, the Sixth Deans Committee Report of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has laid the foundation for a transformational journey in agricultural education in India. Aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, this report is not just a document but a roadmap to empower the next generation of farmers, Agri entrepreneurs and agricultural scientists.
Imagine a world where students learn about traditional farming methods and master cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, and machine learning. A world where they are not only job seekers but also job givers, equipped with the skills to start their agribusiness. Sounds exciting, right? If you are a BSc Agriculture student or you want to pursue a BSc Agriculture or any degree related to agriculture, let’s take a look at the key highlights of this groundbreaking report and find out how it is going to revolutionize agricultural education in India.”
6th Dean Committee Report—Introduction
What is ICAR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research)?
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) works under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education, Government of India and its main objective is to give direction to agricultural education in India, develop high-quality human resources and update the agricultural education system under national and international standards.
ICAR has been continuously updating the agricultural education system through five Deans Committees and now the Sixth Deans’ Committee has been constituted to make it in line with the National Education Policy (NEP-2020).
What is the Sixth Deans’ Committee?
The Sixth Deans’ Committee was constituted by ICAR on 17 August 2021 (order issued on 15 September 2021), with the main objective of redesigning the undergraduate courses (UG Programs) of agricultural education and making it in line with the National Education Policy (NEP-2020)
Now the question is – what has changed?
👉 New course structure
👉 Skill-based learning
👉 Multiple entry-exit system
👉 New subjects like Artificial Intelligence, Robotics
👉 Emphasis on entrepreneurship and industrial training
Objectives of Sixth Deans' Committee
Objective | Details |
Restructuring UG Programs | Updating syllabi of 13 agricultural and allied disciplines as per modern educational needs. |
Alignment with NEP-2020 | Making the curriculum "Light but Tight", focusing on skill-based education. |
Multiple Entry & Exit System | Allowing students to exit with a UG Certificate (1 year), UG-Diploma (2 years), or complete UG Degree (4 years). |
Internships & Practical Learning | Mandatory 10-week internships after 1st and 2nd year to enhance real-world exposure. |
Introduction of Modern Subjects | Adding AI, Robotics, Machine Learning, Agri-IT, Natural Farming, and Agribusiness Management to the curriculum. |
Entrepreneurship & Self-Employment Focus | Encouraging students to become job creators rather than job seekers by integrating business and marketing subjects. |
Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) | Allowing students to store and transfer their academic credits across different institutions. |
Key Differences: 5th Deans' Committee vs. 6th Deans' Committee
Aspect | 5th Deans' Committee (2016) | 6th Deans' Committee (2021) |
Curriculum Framework | Traditional course structure with core agricultural subjects | Aligned with NEP-2020, introducing modern subjects, skill-based education, and flexible learning |
Multiple Entry & Exit System | Not available | Introduced UG-Certificate (1 year), UG-Diploma (2 years), and UG Degree (4 years) with re-entry options |
Internships & Practical Learning | Some hands-on training but not mandatory for UG programs | Mandatory 10-week internships after 1st and 2nd year + industry-linked training in the 4th year |
New Disciplines | Covered traditional agricultural disciplines | Added Natural Farming & Agribusiness Management as new UG programs |
Technology Integration | Limited IT-based courses | Added AI, Robotics, Machine Learning, and Agricultural Informatics for digital-era readiness |
Entrepreneurship & Industry Linkages | Limited focus on agribusiness | Strong emphasis on entrepreneurial skills, agribusiness, and rural enterprise development |
Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) | Not Implemented | Introduced credit storage and transfer system for student mobility |
Online Learning & Digital Courses | Not a major focus | Encourages MOOCs, SWAYAM, Coursera, etc., for additional learning |
Student Mobility & Flexibility | Fixed academic structure | Flexible curriculum, allowing migration between institutions |
Assessment & Examination | Focus on theoretical exams | Progressive assessment, including projects, quizzes, and critical thinking exercises |
Reasons behind syllabus revision and its impact on agriculture students
Have you ever thought about what our agriculture students need to meet the challenges of today—such as climate change, sustainable farming, and technology? The Sixth Deans’ Committee Report has tried to answer this question. The syllabus has been revised to modernize agriculture education so that students not only gain knowledge of traditional farming but are also equipped with modern technologies and entrepreneurship skills.
Main Reasons for Syllabus Revision-
1.Alignment of National Education Policy (NEP) 2020:
“NEP 2020 has emphasized flexibility, skill development, and holistic learning in the education system. It was also necessary to align agriculture education with this policy so that students can be prepared for the challenges of today’s times.”
2. Need for Technology and Innovation:
“Nowadays, the use of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotics, Machine Learning, and Precision Farming is increasing in agriculture. Therefore, these topics have been included in the syllabus, so that students can become familiar with these technologies and apply them in their farming practices.”
3. Skill Development and Employability:
“In the traditional education system, students were only given theoretical knowledge, but there was less focus on practical skills and employability. The new syllabus includes skill enhancement courses, internships, and hands-on training so that students can be prepared for the industry.”
4. Promoting Entrepreneurship:
“To promote entrepreneurship in the agriculture sector, courses like Agribusiness Management and Entrepreneurship Development have been included in the syllabus. This will allow students to start their own business and become job creators.”
5. Sustainability and Natural Farming:
“Keeping in view the climate change and depletion of natural resources, topics like Natural Farming and Sustainable Agriculture have also been included in the syllabus. This will give students knowledge of eco-friendly farming practices.”
Impact On Agriculture Students-
1. Multiple Entry and Exit Options: Flexibility will increase:
“The new syllabus will give students multiple entry and exit options. They can earn a UG Certificate after the first year, a UG Diploma after the second year, or complete a full four-year program to earn a B.Sc. (Hons) Agriculture degree. This will give students flexibility according to their career goals.”
2. Skill Development: Practical Knowledge will be provided:
“Skill enhancement courses and internships have been included in the syllabus. This will give students practical knowledge and hands-on experience, which will prepare them for the industry. They can learn modern farming techniques, agri-tech tools, and business management skills.”
3. Technology-Driven Education: Future-Ready Students:
“The new syllabus includes courses like AI, Robotics, Machine Learning, and Agricultural Informatics. This will give students knowledge of modern technologies, which will make them future-ready.”
4. Entrepreneurship Opportunities: Become Job Creators:
“The syllabus includes courses like Entrepreneurship Development and Agribusiness Management. This will allow students to start their own agribusiness and become job creators. They can start their startups and boost the rural economy.”
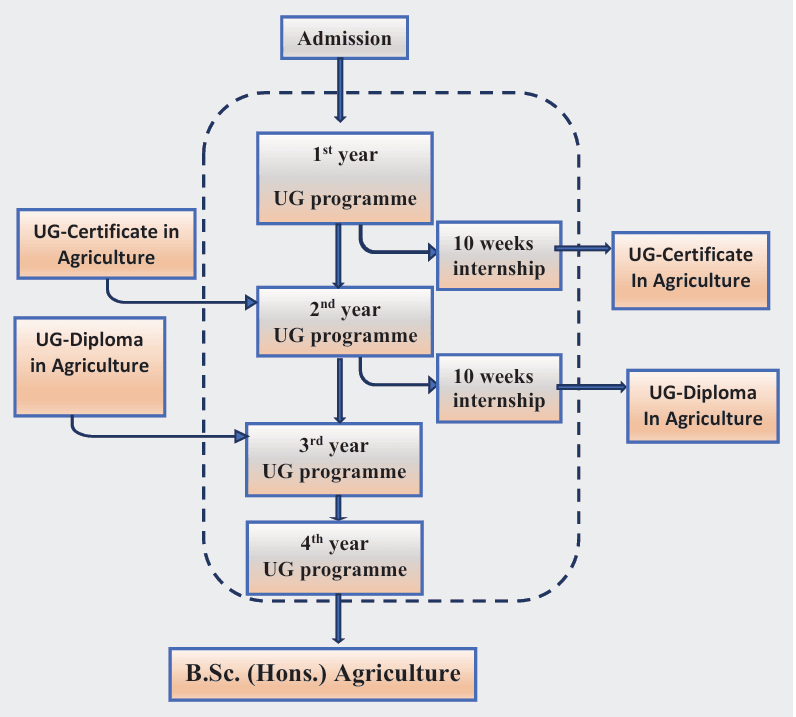
Key Features of 6th Dean Committee agriculture syllabus
If you are studying agriculture or want to make a career in this field, then you need to know that the 6th Dean Committee agriculture syllabus, has made major changes in agricultural education. The purpose of these changes is to connect agricultural students not just with theory, but with real experience and modern techniques. 🚜🌾
Now let’s talk about the main features of this new syllabus, which make it different and better than before. 👇
1️⃣ Multiple Entry-Exit System – Now studies will be more flexible! 🎓🚪
Now students will get the option to continue studying or take a break in between as per their convenience. That is, if for any reason you want to stop studying, then your hard work will not go in vain!
🔹 After 1 year (UG Certificate) – If you complete 2 semesters and do an internship of 10 weeks, then you will get a UG Certificate.
🔹 After 2 years (UG Diploma) – If you complete 4 semesters and do another 10 weeks of internship, you can get a UG Diploma.
🔹 After 4 years (UG Degree – B.Sc. Hons./B.F.Sc. Hons./B.Tech) – You will get a full degree after completing 8 semesters. During this time, you will also get the option of industrial training and specialization.
👉 Now if you stop studying for any reason, then you can come back later and continue from there! This change will be very beneficial for those students who want to work in any other field along with their studies.
2️⃣ New subjects and specialization – Ready for future farming! 🌱🤖
Now farming is not limited to just plough and oxen, but modern technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), robotics, and machine learning have also entered it. The 6th Dean Committee has added some new and important subjects so that students are fully prepared for the farming of the future.
✔ Artificial Intelligence (AI) – for smart farming and data-driven decision-making.
✔ Robotics & Machine Learning – for automation in fields and advanced agricultural equipment.
✔ Agribusiness Management – to help students start their own agricultural business.
✔ Natural Farming – for chemical-free and sustainable farming.
✔ Agricultural Informatics – to promote digital farming and smart agriculture systems.
👉 With these subjects, agriculture students can become not just farmers but also agri-tech experts and agribusiness professionals!
3️⃣ Practical Learning and Internship – No more bookish knowledge! 🏭👨🌾
Now not only will you study in the classroom, but you will also get real experience in the fields and industry! These changes have been made to connect students with field experience, industry training and live projects.
✔ Industry Exposure: Now students will get the opportunity to do internships in agricultural companies, startups and industries.
✔ Rural Agricultural Work Experience (RAWE): Students will get real experience of going to villages and working with farmers.
✔ Experiential Learning:
Hands-on training, research projects, and in-plant training have been made mandatory under the Student READY program in the fourth year.
This will also prepare students to start their own agribusiness instead of looking for a job.
👉 Now students will not only get a degree but also real-life experience so that they can become experts in farming, business and technology!
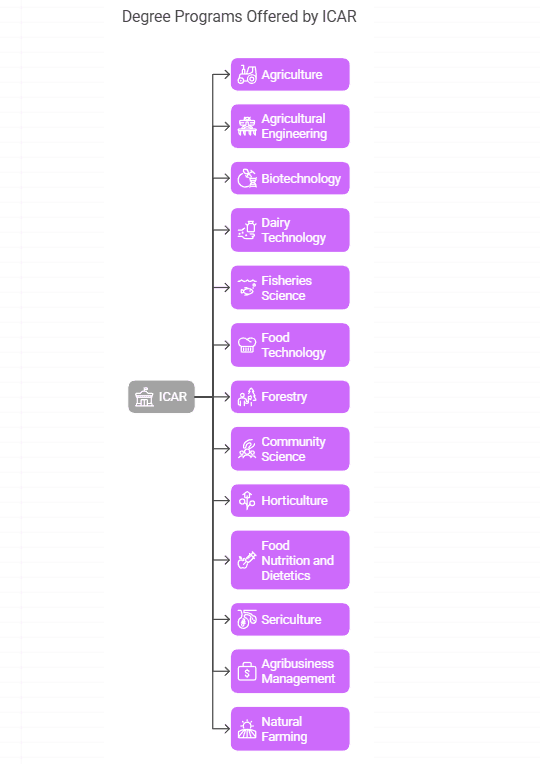
13 Degree programs Run By ICAR
Semester-wise 6th Dean Committee agriculture syllabus
If you are doing or thinking of doing a B.Sc. Agriculture, then the biggest question is – what will have to be studied in the syllabus? 🤔
The good news is that the 6th Deans’ Committee has made agricultural education even more practical, modern and skill-focused. Now in every semester, emphasis has been laid not only on theory but also on practical, industrial training and experience-based learning. 🚜💡
So let’s know the semester-wise 6th Dean Committee agriculture syllabus and how it can make your studies easier and your career better! 👇🔥
Semester I Courses | Credits |
Deeksharambh (Induction cum Foundation Course) | 1 Week (NG) |
Skill Enhancement Course-I | 2(0+2) |
Skill Enhancement Course-II | 2(0+2) |
Communication Skills | 2(1+1) |
Farming-based Livelihood Systems | 3(2+1) |
Rural Sociology & Educational Psychology | 2(2+0) |
Fundamentals of Agronomy | 3(2+1) |
Fundamentals of Soil Science | 3(2+1) |
Fundamentals of Horticulture | 3(2+1) |
NSS-I / NCC-I | 1(0+1) |
Total Credits (Semester I) | 21 (11+10) |
Semester II Courses | Credits |
Skill Enhancement Course-III | 2(0+2) |
Skill Enhancement Course-IV | 2(0+2) |
Personality Development | 2(1+1) |
Environmental Studies & Disaster Management | 3(2+1) |
Soil Fertility Management | 3(2+1) |
Fundamentals of Entomology | 3(2+1) |
Livestock & Poultry Management | 2(1+1) |
Fundamentals of Plant Pathology | 3(2+1) |
NSS-II / NCC-II | 1(0+1) |
Total Credits (Semester II) | 21 (10+11) |
Semester III Courses | Credits |
Skill Enhancement Course-V | 2(0+2) |
Entrepreneurship Development & Business Communication | 3(2+1) |
Physical Education, First Aid, Yoga Practices & Meditation | 2(0+2) |
Principles of Genetics | 3(2+1) |
Crop Production Technology-I (Kharif Crops) | 3(1+2) |
Fundamentals of Extension Education | 2(1+1) |
Production Technology of Fruit & Plantation Crops | 2(1+1) |
Fundamentals of Nematology | 2(1+1) |
Principles & Practices of Natural Farming | 2(1+1) |
Total Credits (Semester III) | 21 (9+12) |
Semester IV Courses | Credits |
Skill Enhancement Course-VI | 2(0+2) |
Agricultural Informatics & Artificial Intelligence | 3(2+1) |
Production Technology of Vegetables & Spices | 2(1+1) |
Principles of Agricultural Economics & Farm Management | 2(2+0) |
Crop Production Technology-II (Rabi Crops) | 3(1+2) |
Farm Machinery & Power | 2(1+1) |
Water Management | 2(1+1) |
Problematic Soils & Their Management | 2(1+1) |
Basics of Plant Breeding | 3(2+1) |
Total Credits (Semester IV) | 21 (11+10) |
Semester IV Courses | Credits |
Skill Enhancement Course-VI | 2(0+2) |
Agricultural Informatics & Artificial Intelligence | 3(2+1) |
Production Technology of Vegetables & Spices | 2(1+1) |
Principles of Agricultural Economics & Farm Management | 2(2+0) |
Crop Production Technology-II (Rabi Crops) | 3(1+2) |
Farm Machinery & Power | 2(1+1) |
Water Management | 2(1+1) |
Problematic Soils & Their Management | 2(1+1) |
Basics of Plant Breeding | 3(2+1) |
Total Credits (Semester IV) | 21 (11+10) |
Semester VI Courses | Credits |
Fundamentals of Agri-Biotechnology | 3(2+1) |
Basic & Applied Agricultural Statistics | 3(2+1) |
Crop Improvement (Rabi Crops) - II | 2(1+1) |
Renewable Energy in Agriculture & Allied Sector | 2(1+1) |
Dryland Agriculture/Rainfed Agriculture & Watershed Management | 2(1+1) |
Agricultural Microbiology & Phyto-remediation | 2(1+1) |
Agricultural Finance & Cooperation | 2(1+1) |
Essentials of Plant Biochemistry | 3(2+1) |
Fundamentals of Seed Science & Technology | 2(1+1) |
Total Credits (Semester VI) | 21 (12+9) |
6th dean committee BSc Agriculture Sevanth Semester Syllabus
Semester VII Courses | Credits |
5 Elective Courses (Major or Minor) each of 4 (3+1) credits | 20(15+5) |
Total Credits (Semester VII) | 20 |
6th dean committee BSc Agriculture 8th Semester Syllabus
Semester VIII Courses | Credits |
Student READY: RAWE/Industrial Attachment/Experiential Learning/Hands-on Training/Project Work/Internship | 20 Credits |
📜6th dean committee BSc Agriculture Skill Enhancement Courses (Indicative List)
Course Title | Credits |
Computer Applications in Agriculture | 2 (0+2) |
Production Technology for Bio-Agents & Bio-Fertilizers | 2 (0+2) |
Seed Production & Seed Testing | 2 (0+2) |
Livestock Production & Management | 2 (0+2) |
Poultry Production Technology | 2 (0+2) |
Development of Agribusiness Proposal | 2 (0+2) |
📜6th dean committee Online Courses Guidelines
Students must complete online courses of at least 10 credits per UGC guidelines.
| Feature | Details |
|---|
| Eligible Courses | Basic Sciences, Humanities, Language, Communication Skills |
| Platforms | MOOCs, SWAYAM, Coursera, edX |
| Approval | Permission of the Dean is required |
| Evaluation | Non-gradial (You will get a separate certificate) |
📌 Department/Section-wise Course Breakup
This is the department-wise description of the Agriculture Graduate Course as per the Sixth Dean Committee. This will give students a clear idea of the courses under each subject. 🚜🌾
Agronomy
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Agronomy | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Farming-based Livelihood Systems | 3 (2+1) |
| 3 | Crop Production Technology-I (Kharif Crops) | 3 (1+2) |
| 4 | Crop Production Technology-II (Rabi Crops) | 3 (1+2) |
| 5 | Water Management | 2 (1+1) |
| 6 | Weed Management | 2 (1+1) |
| 7 | Introductory Agroforestry | 2 (1+1) |
| 8 | Dryland Agriculture / Rainfed Agriculture & Watershed Management | 2 (1+1) |
| 9 | Principles & Practices of Natural Farming | 2 (1+1) |
Soil Science
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Soil Science | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Soil Fertility Management | 3 (2+1) |
| 3 | Problematic Soils & Their Management | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 8 (5+3) |
Horticulture
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Horticulture | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Production Technology of Fruit & Plantation Crops | 2 (1+1) |
| 3 | Production Technology of Vegetables & Spices | 2 (1+1) |
| 4 | Ornamental Crops, MAPs & Landscaping | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 9 (5+4) |
Genetics & Plant Breeding
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Principles of Genetics | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Basics of Plant Breeding | 3 (2+1) |
| 3 | Crop Improvement (Kharif Crops) – I | 2 (1+1) |
| 4 | Crop Improvement (Rabi Crops) – II | 2 (1+1) |
| 5 | Fundamentals of Seed Science & Technology | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 12 (7+5) |
Entomology
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Entomology | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Pest Management in Crops & Stored Grains | 3 (2+1) |
| Total | 6 (4+2) |
Plant Pathology
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Plant Pathology | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Diseases of Field & Horticultural Crops & Their Management | 3 (2+1) |
| 3 | Agricultural Microbiology & Phyto-remediation | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 8 (5+3) |
Extension Education
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rural Sociology & Educational Psychology | 2 (2+0) |
| 2 | Fundamentals of Extension Education | 2 (1+1) |
| 3 | Communication Skills | 2 (1+1) |
| 4 | Personality Development | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 8 (5+3) |
Agricultural Meteorology
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Environmental Studies & Disaster Management | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Introduction to Agro-meteorology | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 5 (3+2) |
Agricultural Economics
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Principles of Agricultural Economics & Farm Management | 2 (2+0) |
| 2 | Entrepreneurship Development & Business Communication | 3 (2+1) |
| 3 | Agricultural Marketing & Trade | 2 (1+1) |
| 4 | Agricultural Finance & Cooperation | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 9 (6+3) |
Agricultural Statistics
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Agricultural Informatics & Artificial Intelligence | 3 (2+1) |
| 2 | Basic & Applied Agri-Statistics | 2 (1+1) |
| 3 | Introductory Mathematics | 1 (1+0) (Non-Gradial) |
| Total | 6 (4+2) |
Agricultural Engineering
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Farm Machinery & Power | 2 (1+1) |
| 2 | Renewable Energy in Agriculture & Allied Sector | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 4 (2+2) |
Nematology
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Nematology | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 2 (1+1) |
Biochemistry
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Essentials of Plant Biochemistry | 3 (2+1) |
| Total | 3 (2+1) |
Crop Physiology
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Crop Physiology | 3 (2+1) |
| Total | 3 (2+1) |
Animal Husbandry
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|
| 1 | Livestock & Poultry Management | 2 (1+1) |
| Total | 2 (1+1) |
Agricultural Bio-Technology
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fundamentals of Agri-Biotechnology | 3 (2+1) |
| Total | 3 (2+1) |
Students' Welfare
| S. No | Course Title | Credit Hours |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NCC/NSS | 1 (0+1) |
| 2 | NCC/NSS | 1 (0+1) |
| 3 | Physical Education, First Aid & Yoga Practices | 2 (0+2) |
| 4 | Study Tour | 2 (0+2) (Non-Gradial) |
| Total | 6 (0+6) |
Evaluation & Examination System
Course Type | External Theory | Internal Theory (Mid-term) | Quiz/Progressive Assessment | Final Practical |
Courses with Theory + Practical | 40% | 20% | 20% | 20% |
Courses with Theory Only | 50% | 30% | 20% | - |
Courses with Practical Only | 30% | 20% | 50% (Internal) | - |
📜 Key Features of the 6th dean Examination System
✅ External Theory Examinations:
- The question papers will be set by external experts.
- The duration of the exam will be 2 to 2.5 hours.
- The assessment will be done by the Head of Department (HoD) under a moderation process.
- The paper assessment will be done by a faculty member who is not the course instructor.
✅ Internal Theory & Practical Examinations:
- The mid-term exam will be of 1 hour.
- The progressive assessment will include quizzes, group assignments, and critical thinking tests.
- The practical examinations will be conducted by the course instructor and a faculty member nominated by the HoD.
✅ Assessment of Skill Enhancement Courses (SEC):
- Will be done like practical-only courses.
✅ Quiz & Progressive Assessment:
- Each subject will have 2 quizzes during the semester –
One before mid-term
Second after mid-term
- If a student scores less than 50% on any one quiz, he/she will get an opportunity to take a third quiz.
✅ Internship Assessment (RAWE/Industrial Training):
- The assessment will be done by the parent institute and the host industry/organization.
- Each will have a 50% weightage.
- The student will have to submit a report and make a presentation in front of other students.
✅ MOOC/Online Courses:
- Completed courses will be indicated in the transcript with a ‘Satisfactory’ remark.
✅ Deficiency Courses:
- If a student takes a deficiency course, it will be assessed as ‘Satisfactory’ or ‘Unsatisfactory’ without any grade points.
✅ Grading System (10-Point Scale):
10 Point = 100 Marks
Grade points will be calculated by dividing the percentage marks of the subject by 10.
✅ Award of Divisions:
OGPA | Division |
5 to <6 | Pass |
6 to <7 | Second Division |
7 to <8 | First Division |
>=8 | First Division with Distinction |
📌 Total Credit Distribution of 6th dean committee syllabus
📜 Important Instructions:
✅ Deeksharambh (Induction cum Foundation Course) – A 2-week non-graded course for student orientation.
✅ Skill Enhancement Courses (SEC) – 6 courses, each carrying 2 credits.
✅ MOOC/Online Courses – Students can complete up to 10 credits through online platforms.
✅ Study Tour – A 10 to 14-day educational tour, non-graded.
✅ Student READY Program – Includes RAWE, Industrial Training, Hands-on Learning, Project Work, and Internship.
people also ask
The B.Sc. Agriculture syllabus covers agronomy, soil science, horticulture, genetics, plant breeding, entomology, pathology, agricultural engineering, economics, extension education, and agribusiness management. It includes AI, robotics, precision farming, natural farming, and organic agriculture. Practical learning through RAWE, industrial training, internships, and experiential learning ensures industry-ready graduates. The program follows NEP-2020 guidelines with a flexible credit system. 🚜
In B.Sc. Agriculture, the passing marks are determined based on the grading system and OGPA (Overall Grade Point Average) set by the university. As per the Sixth Deans’ Committee guidelines:
✅ Minimum Passing OGPA: 5.00 on a 10-point scale
✅ Division Criteria:
- 5.00 to <6.00 – Pass
- 6.00 to <7.00 – Second Division
- 7.00 to <8.00 – First Division
- 8.00 and above – First Division with Distinction
B.Sc. Agriculture is neither too hard nor too easy—it depends on your interest and dedication! 🌱📚
✅ Easy if you:
- Love plants, farming, and technology.
- Enjoy practical learning, fieldwork, and research.
- Stay consistent with studies and internships.
❌ Challenging if you:
- Struggle with biology, chemistry, and technical subjects.
- Find practical fieldwork, data analysis, and research projects difficult.
- Lack interest in agriculture, economics, and agribusiness.
Yes, B.Sc. Agriculture is great for IAS preparation, especially for UPSC optional subjects. It covers agriculture, rural development, and economics, which help in GS papers and Mains. With high success rates, it also provides backup career options in ICAR, FCI, NABARD, and agribusiness. Ideal for those interested in administration, policymaking, and rural development. 🚜📚
Conclusion-
🚀 Final Thoughts – The Future of Agriculture Education is Here!
So friends, that is all about 6th Dean Committee agriculture syllabus and the 6th Dean Committee has completely revamped agriculture education! Now the focus is not just on bookish knowledge, but also on skill-based learning, technology, entrepreneurship and industry exposure. 📚✨
This new syllabus includes advanced topics like AI, robotics, smart farming, natural farming and agribusiness, so that students can be prepared for the challenges of the 21st century. 🎯🌱
👉 Did you like these changes?
👉 Do you think this will give better career opportunities to agriculture students?
👉 What are your thoughts? Comment below and share this information with your friends! 📢👇
Now the time has come to adopt new-age farming – so get ready for this new era of “smart agriculture”!
Click to Join Our Free WhatsApp Group for Agriculture Updates!
Get daily updates, free study material, and the latest schemes, and connect with other agriculture students and farmers.
Read semester wish detailed syllabus
Read latest post-
📚 Cotton Corporation of India syllabus 2025 Notification out for 147 post
“Are you preparing for the Cotton Corporation of India (CCI)...
Read More📋 MPPSC Food Safety Officer Syllabus 2025| Notification Out for 67 Posts
The MPPSC announced 67 vacancies for Food Safety Officers. Suppose...
Read More👉Top 100 Crop Improvement in Rabi Crops MCQs + Fill in Blanks + One Liners (Exam Special)
Crop improvement in rabi crops MCQs is one of the...
Read More👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More



