If you are a B.Sc. Agriculture 1st year student or thinking of taking admission in this course, then the first question in your mind will be—
“What has changed in the syllabus this time?”
And the answer is—a lot!
I am an agriculture student, and when I first got the update of the 6th Dean Committee BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Syllabus, to be honest, there was a bit of confusion and excitement, too. That is why in this blog, I am going to share with you the complete syllabus, course pattern, credit system, and exam structure of the first semester step-by-step—that too in a very easy and understandable language.
This time, the syllabus has been completely changed as per the New Education Policy (NEP-2020)—now the focus is on theory as well as skill development, industry exposure, and digital education. It is important for you to know all this so that you can do the right planning from the beginning.
So let’s get started, knowing what the first semester of BSc Agriculture looks like as per the 6th Dean Committee and how you can complete it wisely! 🚜📘
📘 What is ICAR 6th Dean Committee? – The backbone of the new agriculture syllabus
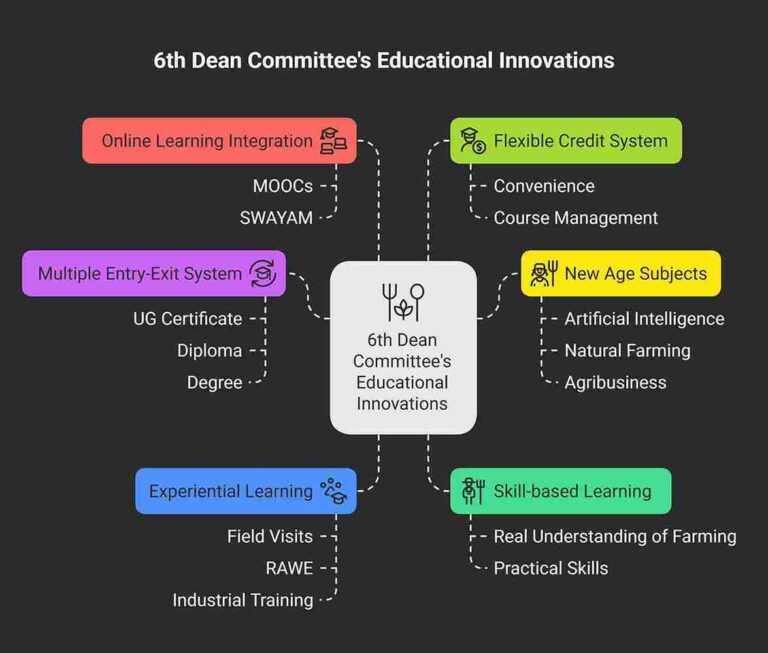
Whenever we talk about the new syllabus 2025 of B.Sc. Agriculture, one name comes up again and again—the 6th Dean Committee. But the question arises, what is this committee? And what does it have to do with the syllabus? Let’s understand it in simple language.
🔍 What is the 6th Dean Committee?
The 6th Dean Committee was constituted by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) on 17 August 2021. Its objective was—
“To make undergraduate courses of the B.Sc. Agriculture and other allied subjects in line with the New Education Policy (NEP-2020).”
This committee comprised leading agricultural educationists and experts of the country, who together reviewed the old syllabus and prepared a new, skill-based, and industry-focused syllabus.
🎯 What did the 6th Dean Committee focus on?
Download 6th Dean Committee report PDF
6th Dean Committee BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Syllabus: The entire semester at a glance
Now that you know what the 6th Dean Committee is and what important reforms it has introduced, let’s talk about the 6th Dean Committee BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Syllabus– the first step of your agriculture journey.
The first semester is designed in such a way that the student can get a good base of basic understanding of agriculture, a connection with agricultural society, and communication and skill development. Also, the balance of theory + practical is maintained well in it. 🎓🌾
6th Dean Committee BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Pattern
Semester I Courses | Credits |
Deeksharambh (Induction cum Foundation Course) | 1 Week (NG) |
Skill Enhancement Course-I | 2(0+2) |
Skill Enhancement Course-II | 2(0+2) |
Communication Skills | 2(1+1) |
Farming-based Livelihood Systems | 3(2+1) |
Rural Sociology & Educational Psychology | 2(2+0) |
Fundamentals of Agronomy | 3(2+1) |
Fundamentals of Soil Science | 3(2+1) |
Fundamentals of Horticulture | 3(2+1) |
NSS-I / NCC-I | 1(0+1) |
Total Credits (Semester I) | 21 (11+10) |
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Deeksharambh syllabus
- Discussions on operational framework of academic process in the University, as well as
interactions with academic and research managers of the University - Interaction with alumni, business leaders, perspective employers, outstanding achievers in
related fields, and people with inspiring life experiences - Group activities to identify the strength and weakness of students (with expert advice for
their improvement) as well as to create a platform for students to learn from each other’s life
experiences - Activities to enhance cultural Integration of students from different backgrounds.
- Field visits to related fields/ establishments
- Sessions on personality development (instilling life and social skills, social awareness, ethics
and values, team work, leadership, etc.) and communication skills
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Communication Skills syllabus
Theory
Communication Process: The magic of effective communication; Building self-esteem and
overcoming fears; Concept, nature and significance of communication process; Meaning, types and
models of communication; Verbal and non-verbal communication; Linguistic and non-linguistic
barriers to communication and reasons behind communication gap/ miscommunication.
Basic Communication Skills: Listening, Speaking, Reading and Writing Skills; Precis writing/
Abstracting/Summarizing; Style of technical communication, Curriculum vitae/resume writing;
Innovative methods to enhance vocabulary,including analogy questions.
Structural and Functional Grammar: Sentence structure, modifiers, connecting words, and
verbal phrases and clauses; Case: subjective case, possessive case, objective case; Correct usage
of nouns, pronouns and antecedents; adjectives; adverbs and articles; Agreement of the verb with the
subject: tense, mood, voice; Writing effective sentences; Basic sentence faults
Practical
Listening and note taking; Writing skills: précis writing, summarising and abstracting; Reading
and comprehension (written and oral) of general and technical articles; Micro-presentations and
Impromptu Presentations: Feedback on presentations; Stage manners: grooming, body language,
voice modulation, speed; Group discussions; Public speaking exercises; vocabulary building
exercises; interview techniques; organization of events.
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Farming Based Livelihood system syllabus
Theory
Status of agriculture in India and different states, Income of farmers and rural people in
India, Livelihood-Definition, concept and livelihood pattern in urban and rural areas, Different
indicators to study livelihood systems. Agricultural livelihood systems (ALS): Meaning, approach,
approaches and framework, Definition of farming systems and farming-based livelihood systems
Prevalent farming systems in India contribute to livelihood. Types of traditional and modern
farming systems. Components of farming systems/farming-based livelihood systemsCrops and
cropping systems, Livestock (Dairy, Piggery, Goatry, Poultry, duckery, etc.), Horticultural crops,
Agro–forestry systems, aquaculture duck/Poultry cum Fish, Dairy cum Fish, Piggery cum Fish
etc., Small-, medium- and large-sized enterprises including value chains and secondary enterprises, as
livelihood components for farmers, Factors affecting integration of various enterprises of farming
for livelihood. Feasibility of different farming systems for different agro-climatic zones, Commercial
farming-based livelihood models by NABARD, ICAR and other organizations across the country,
Case studies on different livelihood enterprises associated with farming. Risk and success factors
in farming-based livelihood systems, Schemes and programs by Central and State Government,
Public and private organizations are are involved in the promotion of farming-based livelihood opportunities.
Role of farming-based livelihood enterprises in the 21st Century because of circular economy, green
economy, climate change, digitalisation and changing lifestyle.
Practical
Survey of farming systems and agricultural based livelihood enterprises, Study of components
of important farming based livelihood models/systems in different agro-climatic zones, Study of
production and profitability of crop-based, livestock-based, processing-based based and integrated farming
Based on on livelihood models, a Field visit to innovative farming system models. Visit of Agri-based
enterprises and their functional aspects for the integration of production, processing and distribution
sectors and Study of agri-enterprises involved in industry and service sectors (Value Chain Models),
Learning about the concept of project formulation on farming-based livelihood systems, along with cost
and profit analysis, case study of start-ups in the agri-sectors.
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Rural Sociology and Educational Psychology syllabus
Theory
Extension Education and Agricultural Extension: Meaning, definition, scope, and importance.
Sociology and rural sociology: Meaning, definition, scope, importance of rural sociology
in Agricultural Extension, and interrelationship between rural sociology and Agricultural Extension
Extension. Indian Rural Society: important characteristics, differences and Relationships Between
rural and urban societies. Social Groups: Meaning, definition, classification, factors considered
information and organization of groups, motivation in group formation and role of social groups
in Agricultural Extension.
Social Stratification: Meaning, definition, functions, basis for stratification, forms of social
Stratification: characteristics and differences between class and caste systems. Cultural concepts:
culture, customs, folkways, mores, taboos, and rituals. Traditions: Meaning, definition and their role
in Agricultural Extension. Social Values and Attitudes: Meaning, definition, types and role of
social values and attitudes in agricultural Extension. Social Institutions: Meaning, definition,
major institutions in rural society, functions, and their role in agricultural Extension. Social
Organizations: Meaning, definition, types of organizations and role of social organizations in
agricultural Extension. Social Control: Meaning, definition, need of social control and means
of social control. Social change: Meaning, definition, nature of social change, dimensions of
social change and factors of social change. Leadership: Meaning, definition, classification, roles
of leader, different methods of selection of professional and lay leaders. Training of Leaders:
Meaning, definition, methods of training, Advantages and limitations in use of local leaders in
Agricultural Extension, Psychology and educational psychology: Meaning, definition, scope,
and importance of educational psychology in Agricultural Extension. Intelligence: Meaning,
definition, types, factors affecting intelligence and importance of intelligence in Agricultural
Extension. Personality: Meaning, definition, types, factors influencing the personality and role
of personality in agricultural Extension. Teaching: Learning process: Meaning and definition of
teaching, learning, learning experience, learning situation, elements of learning situation and
its characteristics. Principles of learning and their implication for teaching
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Fundamentals of Agronomy syllabus
Theory
Agronomy and its scope: Definition, meaning and scope of Agronomy; art, science and
business of crop production, relation of Agronomy with other disciplines of Agricultural Science,
and
fields, crops, and classification; importance, ecology and ecosystem. Seeds and sowing: Definitions
of crops, variety and seed. Factors affecting crop stands establishment: good quality seed, proper
tillage, time of sowing seed rate, depth and method of sowing: broadcasting, drilling, dibbling,
transplanting etc. Tillage and tilth: Definition, objectives, types, advantages and disadvantages of
tillage including conservation tillage. Crop density and geometry: plant geometry and planting
geometry, its effect on growth, yield.
Crop nutrition: Definition of essential nutrients, criteria of essentiality, functional elements,
classification of essential nutrients, role of macro and micro nutrients. Nutrient absorption, active
and passive absorption of nutrients, forms of plant nutrients absorbed by plants, Combined /un
combined forms. Manures and fertilizers, nutrient use efficiency: Sources of nutrients: Inorganic
(fertilizers), organic (manures) and bio-fertilizers; their classification and characteristics, method
of preparation and role of organic manures in crop production. Integrated Nutrient Management
(INM): Meaning, different approaches and advantages of INM. Green manure- role in crop
production: Definition, objectives types of green manuring, desirable characteristics, advantages
and limitations of green manuring.
Water management: Water resources of the world, India and the state; Soil Moisture constants:
gravitational water, capillary water, hygroscopic water, Soil moisture constants.
Weeds: Definition, Importance and basics of classification of weeds and their control. Agro
climatic zones of India and the state, cropping systems: Factors affecting cropping systems, major
cropping patterns and systems in the country. Sustainable crop production: Definition, importance
and practices, natural resources and conservation pollution and pollutants, Allelopathy: Meaning
and importance in crop production, Growth and development of crops: Definition, Meaning and
factors affecting growth and development.
Practical
A visit to the Instructional Crop farm and study on field crops, Identification of crops, seeds,
fertilizers, pesticides, Crops and cropping systems in different Agro-climatic zones of the state,
Study of some preparatory tillage implements, Study of inter tillage implements, Practice of
ploughing / puddling, Study and practice of inter cultivation in field crops, Numerical exercises
on calculation of seed, plant population and fertilizer requirement, Study of yield contributing
characters and yield estimation of crops, Identification of weeds in different crops,
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Fundamentals of Soil Science syllabus
Theory
Soil: Pedological and edaphological concepts. Rocks and minerals, weathering, Silicate clays:
constitution and properties, sources of charge, ion exchange, cation and anion exchange capacity
and base saturation (after buffering capacity), Soil formation, Soil organic matter, Pedogenic
processes, Soil colloids: inorganic and organic, Properties of soil colloids and Ion exchange in
soils, Soil profile, soil texture, soil structure. Bulk density and particle density, soil consistency,
soil temperature, soil air, soil water. Soil reaction and buffering capacity. Soil taxonomy,
keys to soil orders. Soils of India.
Practical
Study of the general properties of minerals, study of minerals-silicate and non-silicate
minerals, study of rocks-igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks; study of a soil profile,
collection and processing of soil for analysis, study of soil texture-feel method, mechanical analysis,
determination particle density and soil porosity, determination of soil colour, study of soil structure
and aggregate analysis, determination of soil moisture, determination of soil moisture constants
field capacity; water holding capacity. Study of infiltration rate of soil, determination of pH and
Electrical conductivity of soil
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Fundamentals of Horticulture syllabus
Theory
Horticulture: Its different branches, importance and scope, Horticulture and botanical
classification, soil and climate for horticultural crops. Plant propagation: methods and propagation
structures, seed dormancy and seed germination, Merits and demerits of sexual and asexual
propagation Stock-scion relationship.
Principles of orchard establishment, principles and methods of training and pruning of fruit
crops, Juvenility and flower bud differentiation, unfruitfulness in horticultural crops, pollination,
pollinizers and pollinators, fertilization and parthenocarpy, importance of bio regulators in
horticultural crops, irrigation and its methods, Fertilizer application in horticultural crops.
Practical
Identification and nomenclature of fruit, Layout of an orchard, pit making and system of
planting, Nursery raising techniques of fruit crops, Understanding of plant propagation structures,
Propagation through seeds and plant parts, Propagation techniques for horticultural crops,
Container, potting mixture, potting and repotting, Training and pruning methods on fruit crops,
Preparation of fertiliser mixture and application, Preparation and application of PGR, Layout of
different irrigation systems, Maturity studies, harvesting, grading, packaging and storage
BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Subject: Introductory Mathematics (Non-gradial) syllabus
Theory:
Algebra: Progressions- Arithmetic, Geometric and Harmonic Progressions. Matrices:
Definition of Matrices, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Transpose and Inverse up to 3rd order
by adjoint method, Properties of determinants up to 3rd order and their evaluation.
Differential Calculus: Definition – Differentiation of function using first principle, Derivatives
of sum, difference, product and quotient of two functions, Methods, Increasing and Decreasing
Functions. Application of Differentiation- Growth rate, Average Cost, and Marginal cost, Marginal
Cost, Marginal Revenue. Partial differentiation: Homogeneous function, Euler’s theorem, Maxima
and Minima of the functions of the form y = f (x) and y = f (x1, x2).
Integral Calculus: Integration -Definite and Indefinite Integrals-Methods- Integration by
substitution, Integration by parts. Area under simple well-known curves.
Mathematical Models: Agricultural systems – Mathematical models – classification of
mathematical models- Fitting of Linear, quadratic and exponential models to experimental data.
What is special in the 1st semester?
✅ Deeksharambh (Induction Program):
1-week non-graded course, which gives students a chance to understand university life, course structure, and goals.
✅ Skill Enhancement Courses (SEC):
Focus on practical skills—like lab work, field practice, computer basics, etc.
✅ Theory + Practical Balance:
Each subject is designed in such a way that you not only get information but also learn how to use it.
✅ Community & Rural Understanding:
A subject like rural sociology helps you understand the village, farmer, and social structure, which is very important for an agriculture graduate.
✅ Total Credits:
There are a total of 21 credits in the 1st semester, which are directly involved in your academic performance.
🎓 Conclusion – 6th Dean Committee BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Syllabus
Now that you have fully understood what changes have been made in the 6th Dean Committee BSc Agriculture 1st Semester Syllabus, which subjects will be taught, and what will be the examination system, now is the time to give the right direction to the preparation.
The first semester is not just a beginning but the foundation of your four-year agriculture career. If you start strong from here, further studies and practical exposure will be easy and rewarding for you.
👉 So what are you waiting for? Adopt this new syllabus, learn skills and move towards becoming a professional agriculture expert!
Click to Join Our Free WhatsApp Group for Agriculture Updates!
Get daily updates, free study material, and the latest schemes, and connect with other agriculture students and farmers.
People also ask
The B.Sc. Agriculture syllabus covers agronomy, soil science, horticulture, genetics, plant breeding, entomology, pathology, agricultural engineering, economics, extension education, and agribusiness management. It includes AI, robotics, precision farming, natural farming, and organic agriculture. Practical learning through RAWE, industrial training, internships, and experiential learning ensures industry-ready graduates. The program follows NEP-2020 guidelines with a flexible credit system. 🚜
In B.Sc. Agriculture, the passing marks are determined based on the grading system and OGPA (Overall Grade Point Average) set by the university. As per the Sixth Deans’ Committee guidelines:
✅ Minimum Passing OGPA: 5.00 on a 10-point scale
✅ Division Criteria:
- 5.00 to <6.00 – Pass
- 6.00 to <7.00 – Second Division
- 7.00 to <8.00 – First Division
- 8.00 and above – First Division with Distinction
B.Sc. Agriculture is neither too hard nor too easy—it depends on your interest and dedication! 🌱📚
✅ Easy if you:
- Love plants, farming, and technology.
- Enjoy practical learning, fieldwork, and research.
- Stay consistent with studies and internships.
❌ Challenging if you:
- Struggle with biology, chemistry, and technical subjects.
- Find practical fieldwork, data analysis, and research projects difficult.
- Lack interest in agriculture, economics, and agribusiness.
Read semester's detailed syllabus
Do you know after bsc agriculture exam syllabus?
Latest Syllabus | Download Here |
IBPS Agriculture Filed Officer | |
NABARD GRADE A | |
Food Corporation of India (FCI) | |
RAEO | |
RHEO | |
Food Inspector | |
IFFCO AGT | |
MP PAT | |
UPSSSC AGTA |
Latest post
👉Top 100 Crop Improvement in Rabi Crops MCQs + Fill in Blanks + One Liners (Exam Special)
Crop improvement in rabi crops MCQs is one of the...
Read More👉 Diseases of Field and Horticultural Crops MCQs True/False, fill in the blanks (With Answers for BSc Agriculture)
Diseases of field and horticultural crops are one of the...
Read More80+ Post Harvest Management MCQs, Fill in the Blanks & Short Questions (Exam-Oriented)
Post harvest management is one of the most important units...
Read MoreR.S. Singh Plant Diseases Book PDF: The “Gift” for Plant Pathology Students
Table of Contents If you are a BSc Agriculture student,...
Read More📑 References
ICAR Sixth Deans’ Committee Report (2023) – Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
🔗 Download PDF from ICAR Official WebsiteModel Curriculum for UG Degree Programmes in Agriculture & Allied Disciplines
🔗 ICAR UG Model Curriculum – ICAR.org.inNational Education Policy (NEP) 2020—Ministry of Education, Government of India
🔗 Read Full NEP-2020 Document